Новая коронавирусная инфекция (НКИ) является одной из наиболее актуальных проблем современного здравоохранения. За 2 года пандемии COVID-19 в мире зарегистрировано свыше 6 млн. летальных исходов. Клинические проявления НКИ разнообразны, от бессимптомного до тяжелого и крайне тяжелого течения с развитием острого респираторного дистресс-синдрома и полиорганной дисфункции. Течение и развитие серьезных осложнений при НКИ определяются типом иммунного реагирования организма на инфицирование. Именно адекватный противовирусный иммунный ответ определяет течение и исход инфекции, вызванной SARS-CoV-2. Дефектный ответ интерфероновой системы, наблюдающийся при COVID-19, приводит к дисрегуляции цитокиновой системы и обусловлен синдромом активации макрофагов, усиливающих воспаление и легочную иммунопатологию, а также секрецию большего количества цитокинов [1–3].
Тяжелое течение НКИ сопровождается более выраженным повышением MIP-1a, MIP-1b в сыворотке крови, что позволяет рассматривать эти показатели в качестве потенциальных маркеров тяжелого течения COVID-19 [4]. Отмечена прямая корреляция уровней С-реактивного белка (СРБ), лактатдегидрогеназы (ЛДГ) и ферритина с тяжестью НКИ, распространенностью воспалительной инфильтрации и прогнозом [5, 6].
По современным представлениям, центральной клеткой, регулирующей иммунные и воспалительные реакции, является макрофаг. Основной причиной, определяющей фундаментальную роль макрофагов в защитной системе организма, является их ключевое положение в тканевом гомеостазе. Возможности этих клеток включают ряд важных функций, благодаря которым они занимают ключевые позиции во всех формах иммунного ответа: в продукции антител, индукции и регуляции клеточных иммунных реакций, формировании иммунологической памяти, иммунологической толерантности и вполне оправдывают название «клетки-диспетчера» [7–10].
В настоящее время имеются убедительные клинические и экспериментальные данные, полученные при использовании некоторых иммуномодуляторов, стимулирующий эффект которых выражается в активации системы фагоцитирующих макрофагов (СФМ) [11,12].
Показана способность некоторых иммуномодуляторов оказывать направленное мембраностабилизирующее действие через систему мононуклеарных фагоцитов, которая избирательно и обратимо ингибирует синтез гиперактивированными макрофагами провоспалительных цитокинов (ИЛ-1β, ИЛ-6, ФНО-α), а также стимулирует фагоцитарную активность макрофагов и нейтрофилов при ее исходной недостаточности, активируя «завершенность» фагоцитоза [13, 14].
Многочисленные исследования показали, что тяжесть и исходы COVID-19 тесно связаны с иммунными реакциями организма пациента, часто неуправляемыми и неконтролируемыми, что подчеркивает настоятельную необходимость дальнейшего изучения и понимания всего спектра иммунных нарушений, вызванных вирусом SARS-CoV-2 [15–17].
Высокие уровни экспрессии провоспалительных цитокинов и хемокинов были обнаружены у пациентов с тяжелыми формами COVID-19. Эти воспалительные цитокины могут активировать клеточный иммунный ответ, что является ключевым событием в активации специфического иммунитета. Однако в отличие от пациентов с атипичной пневмонией у пациентов с COVID-19 также повышены уровни и противовоспалительных цитокинов (ИЛ-4, ИЛ-10) [15, 18, 19]. В период пандемии COVID-19, все мировые научные разработки нацелены на изучение патогенеза и поиск наилучших методов лечения [20, 21]. Раскрытие центральной роли макрофагов во многих физиологических и патофизиологических процессах создает предпосылки для целенаправленной иммунорегуляции функции клеток моноцитарно-макрофагального ряда, что может переводить патологический процесс при COVID-19 в физиологическое русло.
Перспективным препаратом направленного действия является аминодигидрофталазиндион натрия (галавит) – отечественный иммуномодулятор, который широко применяется в клинической практике с 90-х гг. ХХ в. Галавит – синтетический иммуномодулятор с противовоспалительным свойством, механизм его действия связан со способностью регулировать функционально-метаболическую активность клеток врожденного и адаптивного иммунитета. В многочисленных клинических исследованиях более чем за 25 лет показано, что препарат повышает резистентность организма к инфекционным заболеваниям различной этиологии, способствует более быстрой элиминации возбудителя из организма, сокращает выраженность и длительность инфекционно-воспалительного процесса, частоту рецидивов инфекций, а также нормализует антителообразование, повышает функциональную активность (аффинитет) антител, опосредованно регулирует выработку клетками-продуцентами эндогенных интерферонов (ИФН-α и -γ) [14, 21, 22].
Целью исследования явилось определение эффективности применения галавита для профилактики и лечения НКИ.
Материалы и методы
На базе клинического отдела инфекционной патологии Центрального НИИ эпидемиологии Роспотребнадзора (далее – ЦНИИЭ) проведено простое наблюдательное описательное исследование в 2 этапа после одобрения ЛЭК. Все участники исследования подписали информированное добровольное согласие на обработку персональных данных и медицинское вмешательство.
На 1-м этапе исследования под наблюдением с октября по декабрь 2020 г. находились 115 работников медицинских учреждений в возрасте от 20 до 60 лет. Из них 68 чел. (основная группа) в профилактических целях получили курс аминодигидрофталазиндиона натрия (галавит; ООО «СЭЛВИМ», Россия) в таблетках по 100 мг в сутки в течение 10 дней. Группу сравнения составили 47 медиков, которые отказались от профилактического курса. У всех участников для определения доли заболевших и сроков инфицирования. еженедельно в течение 1 мес. наблюдения исследовали мазки из носо- и ротоглотки на РНК SARS-CoV-2 методом ПЦР с использованием набора реагентов «АмплиСенс® Cov-Bat-FL» (ЦНИИЭ, Москва).
Полученный выраженный профилактический эффект препарата позволил рекомендовать его в составе комплексной терапии заболевшим НКИ медицинским работникам.
На 2-м этапе исследования в течение 2021 г. под наблюдением находились 76 амбулаторных больных COVID-19 со среднетяжелым течением из числа медработников, из которых 46 (основная группа) в комплексной терапии получали аминодигидрофталазиндион натрия (18 чел. в виде свечей, 28 чел. – в таблетках) в дозе 100 мг в сутки в течение 10 дней, и 30 больных (группа сравнения), получавших стандартную терапию согласно действующим временным методическим рекомендациям (ВМР).
Обследование инфицированных проводили согласно ВМР «Профилактика, диагностика и лечение новой коронавирусной инфекции (COVID-19)» [23]. Инструментальная диагностика включала пульсоксиметрию с измерением SpO2 для выявления дыхательной недостаточности и оценки выраженности гипоксемии, а также компьютерную томографию (КТ) органов грудной клетки у всех заболевших. Диагноз НКИ был установлен на основании выявления РНК SARS-CоV-2 методом ПЦР в мазках из носо- и ротоглотки (100%). Всем пациентам проведены исследования в динамике (в день лабораторного подтверждения диагноза НКИ и через 2 нед. от начала терапии). Лабораторный анализ включал, кроме стандартных методов, исследование уровней противовоспалительных цитокинов – ИЛ-1, -10, -6, ФНО-α и ИФН-α в сыворотке крови методом твердофазного ИФА. Использовали наборы Bioscience (Thermo Fisher Scientific, США) с автоматической обработкой микропланшетным ридером Anthos 2020 (Anthos Labtec Instruments GmbH, Австрия) при длине волны 450 нм с коррекцией 620 нм с построением стандартной кривой оптической плотности и определением концентрации исследуемых цитокинов согласно инструкциям от производителя.
Для статистической обработки данных использовали программы Microsoft Office Excel 2016 (Microsoft) и библиотеки Matplotlib и Numpy среды программирования Python.
Результаты
На 1-м этапе средний возраст медицинских работников составил 41,2 ± 6,7 года. Пациенты основной группы (n = 68) принимали галавит сублингвально по 2 таблетки 2 раза в день (суточная доза – 100 мг) в течение 10 дней, в группе сравнения (n = 47) профилактического курса пациенты не получали. За период наблюдения в основной группе были инфицированы вирусом SARS-CoV-2 14 (20,5%) чел., в то время как в группе сравнения – 22 (46,8%). Полученные данные указывают на профилактическую активность препарата у работников медицинских учреждений в условиях пандемии. Число заболевших и сроки выявления РНК вируса SARS-CoV-2 представлены в таблице.
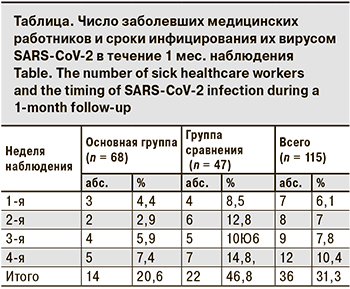
В основной группе у 3 (21,4%) пациентов НКИ протекала бессимптомно, у 5 (35,7%) на фоне клинической картины отсутствовали поражения легких по данным КТ, у 5 (35,7%) регистрировали КТ-1 и у 1 (7,1%) – КТ-2 без проявлений дыхательной недостаточности (SpO2 ≥ 96). При этом в группе сравнения не выявлено бессимптомного течения болезни, только у 2 (9,1%) инфицированных с клиническими проявлениями НКИ не обнаружено поражения легких по данным КТ, у 13 (59,1%) больных выявлено КТ-1, у 5 (22,7%) – КТ-2 и у 2 (9,1%) – КТ-3. Трое (13,6%) заболевших из группы сравнения были госпитализированы на 5–7-е сутки амбулаторного лечения в связи с прогрессированием дыхательной недостаточности (SpO2 ≤ 95) и КТ-3.
Полученный на 1-м этапе исследования выраженный профилактический эффект иммуномодулятора у медицинских работников в условиях пандемии позволил в 2021 г. рекомендовать препарат в комплексной терапии больных COVID-19 со среднетяжелым течением.
Средний возраст участников 2-го этапа исследования (n = 76) составил 48,7 ± 8,1 года. В основную группу (n = 46) вошли 20 мужчин и 26 женщин, получающих с момента обращения и лабораторного подтверждения COVID-19 аминодигидрофталазиндион натрия в комплексной терапии. На 5–7-е сутки от начала заболевания препарат назначали в виде: внутримышечных инъекций по 100 мг 10 дней или сублингвально по 2 таблетки (50 мг) 2 раза в сутки в течение 10 дней. Группа сравнения (n = 30) получала стандартную терапию согласно ВМР [23].
Терапевтическую эффективность препарата оценивали на основании анализа динамики клинико-лабораторных показателей и степени выраженности поражения легких по данным КТ.
39 (51,3%) из 76 пациентов указали на сопутствующие заболевания: сердечно-сосудистой системы 17 (22,4%), дыхательной системы – 9 (11,8%), бронхиальную астму – 3 (3,9%), ожирение – 4 (5,3%), сахарный диабет – 3 (3,9%). Наиболее отягощенной по коморбидности была группа пациентов в возрасте от 40 до 50 лет. Зачастую пациенты старше 55 лет имели сочетанную сопутствующую патологию.
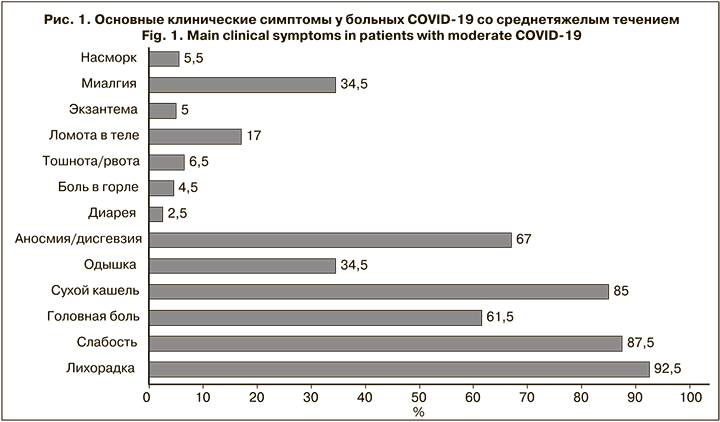
Клинические проявления COVID-19 среднетяжелого течения у амбулаторных больных медработников представлены на рис. 1.
По результатам обследования больных НКИ среднетяжелого течения определяли: уровень лейкоцитов от 3,9 до 17,6×109/л, в среднем – 8,5 ± 3,6×109/л; лейкопению у 18% пациентов, а лейкоцитоз – у 37%); уровень эритроцитов в среднем составил 4,12 ± 0,85×1012/л; показатель тромбоцитов в среднем – 190,41 ± 79,12×109/л. Уровень СРБ находился в диапазоне от 3 до 56 мг/л, в среднем – 14,8 ± 9,6 мг/л; показатель ферритина – от 129,1 до 459,7 мкг/л, в среднем – 378,4 ± 47,6 мкг/л; среднее значение ЛДГ было 217,7 ± 52,1 ЕД/л.
У большинства пациентов при COVID-19 выявлены изменения в анализах крови: повышение уровней СРБ (р < 0,01), D-димера, ЛДГ, ферритина, умеренная тромбоцитопения, повышение показателей АЛТ и АСТ (р < 0,01).
При этом отмечено повышение АЛТ и АСТ до 3 норм у всех пациентов на фоне приема фавипиравира. Показатели трансаминаз нормализовались в основной группе, в то время как в группе сравнения к концу лечения они еще оставались выше референсных значений.
На фоне приема аминодигидрофталазиндиона натрия отмечена положительная динамика лабораторных показателей. Так, уровень СРБ достоверно снизился до 6,8 ± 1,2 мг/мл (р < 0,05), у пациентов с лейкоцитозом нормализовался уровень лейкоцитов – с 15,62 ± 7,1×109/л до 6,39 ± 1,45×109/л, у 26% больных НКИ отмечено купирование лимфопении (до 1,9 ± 0,4×109/л.)
Повреждение легочной ткани различной степени по данным КТ наблюдали у 54 (71,1%) пациентов. В соответствии с принятой градацией по объему поражения легочной ткани были установлены следующие степени поражения легких у больных: КТ-0 – у 22 (28,9%) чел., КТ-1 – у 26 (34,2%), КТ-2 – у 18 (23,7%) и КТ-3 у 10 (13,2%). Были госпитализированы 4 пациента из группы сравнения с нарастанием дыхательной недостаточности и прогрессированием повреждения легких с КТ-0 до КТ-2 за 5 дней наблюдения. Все пациенты имели патологию сердечно-сосудистой системы, ожирение 1–2-й степени, 1 пациент был с бронхиальной астмой и артериальной гипертензией. В основной группе госпитализирована 1 пациентка 58 лет из группы риска по развитию тяжелого течения (сахарный диабет 2-го типа, индекс массы тела > 35 кг/м2) на 3-й день болезни: после проведения КТ органов грудной клетки установлено поражение легких КТ-3.
В конце лечения остаточные жалобы на астенизацию, снижение концентрации внимания и диспептические нарушения сохранились у 24% больных основной группы и у 47% пациентов в группе сравнения, которые еще отмечали слабость, миалгию, нарушения вкуса и обоняния, остаточный сухой кашель и снижение качества жизни. При этом отсутствие регресса поражения легких через 1 мес. наблюдали у 30% больных в группе сравнения. После лечения в большинстве случаев в основной группе отмечено снижение степени повреждения легких по данным КТ органов грудной клетки. Так, удельный вес больных с поражением легких КТ-3 уменьшился с 23,7 до 7,9%. Важно отметить, что у 9 (30%) пациентов в группе сравнения и у 5 (10,9%) больных основной группы отсутствовал регресс повреждения легких.
Анализ состояния цитокиновой системы показал, что у больных со среднетяжелым течением COVID-19 имеется выраженный дисбаланс в продукции цитокинов и хемокинов. У 68% пациентов на фоне достоверно сниженной продукции ИФН-α, значимо повышен уровень ИЛ-10 при незначительном увеличении у 1/3 пациентов уровня ИЛ-6, имевшего тенденцию к достоверному нарастанию при прогрессировании заболевания.
У всех госпитализированных больных COVID-19 был неопределяемый уровень ИФН-α на фоне повышенных концентраций ИЛ-10, -6, -1. В то же время у пациентов с бессимптомным и легким течением отмечалась тенденция к повышению количества ИФН-α при неопределяемых концентрациях ФНО-α, ИЛ-1 и низких уровнях ИЛ-6 и -10.
Обобщая полученные данные, можно заключить, что при среднетяжелом течении CОVID-19 отмечаются дефекты функционирования противовирусной иммунной защиты и дисбаланс цитокинов: недостаточная продукции ИФН-α на фоне достоверного увеличения уровня ИЛ-10 с тенденцией к нарастанию концентраций ИЛ-6, ИЛ-1 и ФНО-α, что негативно влияет как на количество, так и на функциональные возможности адекватного иммунного ответа на инфицирование вирусом SARS-CoV-2.
Динамика показателей цитокиновой системы в зависимости от терапии (рис. 2 см. на вклейке) показала выраженную иммуномодулирующую эффективность галавита, применение которого сопровождалось повышением концентрации ИФН-α и нормализацией уровней ФНО-α, ИЛ-10, ИЛ-6, что значительно улучшает прогноз и способствует ускорению выздоровления.
Обсуждение
Полученные в ходе исследования данные соответствуют современному подходу к профилактике ОРВИ с применением препаратов, повышающих защитные силы организма, способствующих созданию барьера на пути проникновения вируса, и совпадают с результатами исследований других авторов, указавших на выраженный эффект иммуномодулятора галавита в профилактике тяжелого течения и в терапии НКИ [13, 21, 24, 25]. Так, С.В. Колесов и соавт. [21], исследуя эффективность препарата в профилактике COVID-19 у медицинских работников, осуществляющих деятельность в «красной зоне» стационара в условиях высокого риска заражения SARS-CoV-2, выявили достоверное снижение частоты развития средних и тяжелых форм заболевания (16,6% против 28,5%).
Включение в комплексную терапию аминодигидрофталазиндиона натрия оказывает эффективное воздействие на иммунные и функциональные механизмы клеточной защиты организма и положительно влияет на течение инфекции с нормализацией функционально-метаболических процессов в макрофагах и опосредованно через СФМ – на иммунологическую реактивность.
Полученные данные о закономерных изменениях клинико-лабораторных показателей, активации врожденного звена иммунитета, нормализации функциональной активности СФМ с устранением дисбаланса в цитокиновом статусе свидетельствуют об эффективности галавита как препарата патогенетического звена для профилактики и терапии НКИ. Особое значение имеют возможности предупреждения прогрессирования легочных осложнений и уменьшение повреждающего действия легочной ткани с возможным ускорением разрешения внутрилегочных инфильтратов на фоне приема галавита, что обнадеживает в вопросе предотвращения пневмофиброза и профилактики постковидных состояний [13, 21–25]. Возможности регуляции неадекватного иммунного ответа, вызванного вирусом SARS-CoV-2, с применением иммуномодуляторов направленного действия требуют дальнейших глубоких исследований как для поиска новых терапевтических возможностей, так и для воздействия на отдаленные последствия перенесенной НКИ.
Заключение
Иммунный ответ у больных CОVID-19 характеризуется преимущественно супрессированной направленностью и низкой функциональной активностью механизмов противовирусной иммунной защиты, что не обеспечивает адекватного ответа иммунной системы на инфекционно-воспалительный процесс. Назначение иммуномодулятора аминодигидрофталазиндиона натрия (галавита) в дозе 100 мг в сутки для профилактики и лечения НКИ у больных со среднетяжелым течением представляется рациональным и патогенетически обоснованным.


