Заболеваемость острым гепатитом В (ОГВ) в России с 2000 г. снизилась в 33 раза благодаря внедрению активной иммунизации и эффективным профилактическим и противоэпидемическим мерам, но остается проблема хронического гепатита этой этиологии (ХГВ). По оценке Федеральной службы по надзору в сфере защиты прав потребителей и благополучия человека, в Российской Федерации в 2015 г. было выявлено менее 2000 случаев ОГВ (из них 22 случая – среди детей), что составило 1,12 случая на 100 тыс. населения. В настоящее время высокая эпидемиологическая и социально-экономическая значимость вирусных гепатитов в Российской Федерации определяется ежегодной регистрацией их впервые выявленных хронических форм. В 2015 г. заболеваемость ХГВ составила 10,8 на 100 тыс. населения, что в 9 раз превышает показатель заболеваемости ОГВ, хотя в динамике за последние 5 лет наблюдается некоторая тенденция к снижению заболеваемости ХГВ [1, 2].
 Актуальность ХГВ обусловлена риском развития неблагоприятных исходов: у 15–40% инфицированных в будущем возможно развитие таких осложнений, как цирроз печени и гепатоцеллюлярная карцинома (ГЦК) [3, 4]. По мнению А.В. Исакова и соавт. [5], Россия находится на пороге эпидемии поздних осложнений гепатита В. ГЦК занимает 5-е место у мужчин и 8-е место у женщин среди всех злокачественных новообразований [6]. Ежегодно, по данным ВОЗ, от гепатита В умирает 1 млн человек, этот показатель занимает 1-е место среди причин смерти больных с патологией печени [6, 7]. Факторами, предрасполагающими к увеличению риска развития цирроза печени и ГЦК у пациентов с ХГВ, являются пожилой возраст, мужской пол, наследственная предрасположенность к ГЦК, высокий уровень ДНК ВГВ, потребление алкоголя (даже умеренное), коинфекция вирусами гепатитов С, D и ВИЧ [8–10] Наиболее губительным фактором для печени является систематическое злоупотребление алкоголем [10]
Актуальность ХГВ обусловлена риском развития неблагоприятных исходов: у 15–40% инфицированных в будущем возможно развитие таких осложнений, как цирроз печени и гепатоцеллюлярная карцинома (ГЦК) [3, 4]. По мнению А.В. Исакова и соавт. [5], Россия находится на пороге эпидемии поздних осложнений гепатита В. ГЦК занимает 5-е место у мужчин и 8-е место у женщин среди всех злокачественных новообразований [6]. Ежегодно, по данным ВОЗ, от гепатита В умирает 1 млн человек, этот показатель занимает 1-е место среди причин смерти больных с патологией печени [6, 7]. Факторами, предрасполагающими к увеличению риска развития цирроза печени и ГЦК у пациентов с ХГВ, являются пожилой возраст, мужской пол, наследственная предрасположенность к ГЦК, высокий уровень ДНК ВГВ, потребление алкоголя (даже умеренное), коинфекция вирусами гепатитов С, D и ВИЧ [8–10] Наиболее губительным фактором для печени является систематическое злоупотребление алкоголем [10]
Однако на сегодняшний день нет однозначного суждения об интерпретации активности аминотрансфераз как критерии тяжести течения ХГВ и прогностического фактора развития неблагоприятных исходов. При острых вирусных гепатитах степень повышения активности аланинаминотрасферазы (АЛТ), как правило, пропорциональна степени разрушения гепатоцитов и тяжести заболевания, а при хронических формах болезни возможно прогрессирование поражения печени и при низкой активности АЛТ в сыворотке крови [11, 12]. Тем не менее нет общепринятого мнения о соответствии активности АЛТ и прогрессирования ХГВ, особенно при нормальных значениях этого фермента [13,14].
 Цель нашего исследования – выявление клинического значения уровня активности АЛТ у больных ХГВ. Исследование проводили в несколько этапов:
Цель нашего исследования – выявление клинического значения уровня активности АЛТ у больных ХГВ. Исследование проводили в несколько этапов:
- Выявление HBsAg-позитивных лиц.
- Анализ гендерного и возрастного состава в зависимости от активности АЛТ.
- Оценка активности АЛТ у HBsAg-позитивных лиц с наличием ДНК ВГВ в сыворотке крови.
- Сравнительная оценка активности АЛТ и уровня ДНК ВГВ в сыворотке крови.
- Исследование сывороток крови контрольной группы больных ХГВ.
- Оценка степени фиброза печени у HBsAg-позитивных лиц с нормальным значением АЛТ.
Материалы и методы
Для выявления инфицированности ВГВ серологическим методом было обследовано 252 614 человек. Далее у 10 347 HBsAg-позитивных пациентов определяли активность АЛТ биохимическим методом, качественное и количественное содержание ДНК ВГВ в сыворотке крови – молекулярно-биологическим методом. Данное исследование проводили с помощью набора реагентов «АмплиСенс® HBV-FRT» (Центральный НИИ эпидемиологии Роспотребнадзора, Россия) для выявления ДНК ВГВ в клиническом материале методом полимеразной цепной реакции (ПЦР) с гибридизационно-флуоресцентной детекцией в режиме реального времени. Аналитическая чувствительность набора реагентов – 30 МЕ/мл. У части больных с нормальными значениями АЛТ и определяемой ДНК ВГВ в сыворотке крови проводили неинвазивное измерение степени фиброза печени. Исследование проводили с использованием транзиентной фиброэластометрии на аппарате «ФиброСкан» компании «Echosens» (Франция).
Результаты и обсуждение
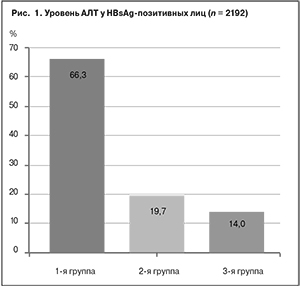
В результате серологического обследования HBsAg обнаружен у 10 347 человек, что составляет 4,1% от числа принявших участие в исследовании. Активность АЛТ исследовали у 2192 HBsAg-позитивных лиц. Нормальный уровень АЛТ определялся у 1455 (66,3%) человек, повышенный – у 737 (33,7%). По уровню активности АЛТ пациенты были распределены в 3 группы:
- 1-я группа – АЛТ ≤ 40 Ед/л (не превышает норму – N);
- 2-я группа – АЛТ > 40 Ед/л, но ≤ 80 Ед/л (не выше 2 N);
- 3-я группа – АЛТ > 80 Ед/л (выше 2 N).
Результаты распределения представлены на рис. 1
 По гендерному составу пациенты распределились так: в 1-й группе было 52,2% мужчин и 47,8% женщин, во 2-й – 74,0 и 26,0% соответственно, в 3-й – 77,1и 22,9%.
По гендерному составу пациенты распределились так: в 1-й группе было 52,2% мужчин и 47,8% женщин, во 2-й – 74,0 и 26,0% соответственно, в 3-й – 77,1и 22,9%.
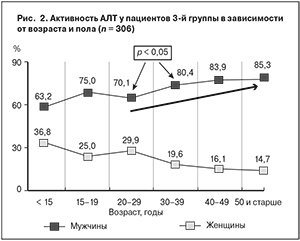
Анализ активности АЛТ в зависимости от возраста не выявил каких-либо значимых тенденций: в возрастных группах 20–29 и 30–39 лет уровень АЛТ > N определялся у 35,9% пациентов, в группе 40–49 лет – у 33,4%, в группе старше 50 лет – у 25,5%. Однако учитывая, что возраст пациента и мужской пол являются независимыми предикторами повышенного риска развития осложнений ХГВ, мы проанализировали эти 2 параметра одновременно у больных 3-й группы. С наименьшей частотой (63,2%) уровень АЛТ > 2 N был выявлен у лиц мужского пола в возрасте до 15 лет – 63,2%. Начиная с 30 лет частота выявления высоких показателей АЛТ возрастает (рис. 2).
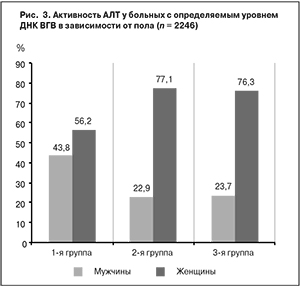
Активность АЛТ исследовали в 2246 образцах сывороток крови, содержащих HBsAg и ДНК ВГВ (качественный анализ). У 1462 (65,1%) пациентов уровень АЛТ не превышал норму. Повышение активности АЛТ разной степени выраженности выявлено у 784 (34,9%) пациентов, из них мужчины составляли 76,8%, женщины – 23,2%. Это соотношение отражает ферментативную активность в одинаковых пропорциях во 2-й и 3-й группах (рис. 3).
Учитывая, что одним из основных прогностических критериев ХГВ является уровень виремии (вирусная нагрузка), мы проанализировали результаты обследования 2676 пациентов (1713 мужчин и 963 женщин), включающие определение активности АЛТ и количественную оценку ДНК ВГВ в сыворотке крови.
В 1-ю подгруппу вошли 2142 (80,0%) пациента с уровнем ДНК ВГВ < 20 000 МЕ/мл, во 2-ю – 534 (20,0%) пациента с уровнем ДНК ВГВ ≥ 20 000 МЕ/ мл.
В 1-й подгруппе нормальный уровень АЛТ определялся у 1598 (74,6%) человек (мужчин 58,6%), повышенный до 80 Ед/л – у 369 (17,2%) человек (мужчин 81,3%), > 2 N – у 175 (8,2%) человек (мужчин 80,6%), то есть признаки поражения печени отмечены у 25,4% пациентов.
Во 2-й подгруппе нормальный уровень АЛТ определялся лишь у 170 (31,8%) человек, повышенный до 2 N – у 179 (33,5%), > 2 N – у 185 (34,6%). Повышенный уровень АЛТ выявляли в этой подгруппе достоверно чаще, чем в 1-й (при АЛТ < 2 N p < 0,05; при АЛТ > 2 N p < 0,01).
 Во 2-й подгруппе нормальные показатели АЛТ выявляли с практически равной частотой у мужчин и у женщин – в 48,8 и 51,2% случаев соответственно. Среди пациентов с повышенным уровнем АЛТ доля мужчин возрастала, но не так значительно, как в 1-й подгруппе: в подгруппе с уровнем АЛТ < 2 N мужчины составляли 64,8%, в подгруппе с уровнем АЛТ > 2 N – 73,5%.
Во 2-й подгруппе нормальные показатели АЛТ выявляли с практически равной частотой у мужчин и у женщин – в 48,8 и 51,2% случаев соответственно. Среди пациентов с повышенным уровнем АЛТ доля мужчин возрастала, но не так значительно, как в 1-й подгруппе: в подгруппе с уровнем АЛТ < 2 N мужчины составляли 64,8%, в подгруппе с уровнем АЛТ > 2 N – 73,5%.
В 1-й подгруппе нормальные показатели АЛТ были у большинства пациентов во всех возрастных группах. Повышенный уровень АЛТ чаще всего (в 28,2% случаев) был отмечен у пациентов в возрасте 20–29 лет. Во 2-й подгруппе, наоборот, у большинства обследованных показатели АЛТ превышали норму. При этом с увеличением возраста частота выявления повышенных показателей АЛТ практически постоянно возрастала: от 55,9% в группе 15–19 лет до 84,2% у пациентов, чей возраст превышал 50 лет (p < 0,01).
Во 2-й подгруппе уровень АЛТ > 2 N был у 25–35% больных в возрасте до 50 лет. У пациентов старше 50 лет такая активность АЛТ отмечалось уже у 47,5% обследованных.
В контрольной группе, в которую вошли 83 пациента с определяемыми более 6 мес. HBsAg и ДНК ВГВ в сыворотке крови, было проведено комплексное клинико-эпидемиологическое лабораторно-инструментальное обследование. В группе было 50 (60,2%) мужчин и 33 (39,8%) женщины в возрасте от 18 до 62 лет. Повышенный уровень АЛТ зарегистрирован у 43 (51,8%) человек: < 2 N – у 14 (16,9%) , > 2 N – у 29 (34,9%).
Минимальная вирусная нагрузка (60 МЕ/ мл) была выявлена у 5 пациентов, максимальная (300 000 000 МЕ/мл) – у 1. Низкая вирусная нагрузка (> 20 000 МЕ/мл) выявлена у 51 (61,4%) пациента, высокая (≥ 20 000 МЕ/мл) – у 32 (38,6%).
У 76,5% пациентов с низкой вирусной нагрузкой определялся нормальный уровень АЛТ, а среди пациентов с высокой вирусной нагрузкой –только 3,1%. Активность АЛТ в пределах 2 N при низкой вирусной нагрузке определялось в 17,6% случаев, при высокой – в 15,6%.
Наиболее значительные различия выявлены у пациентов с активностью АЛТ > 2 N: при низкой вирусной нагрузке этот показатель равнялся 5,9%, при высокой – 81,3%.
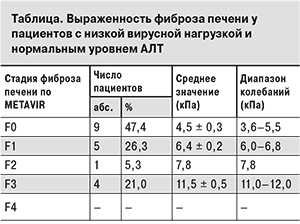
Таким образом, было выявлено, что повышение активности АЛТ при ХГВ чаще регистрируется у мужчин, а также при высокой вирусной нагрузке. Из данных литературы [13, 14] известно, что прогрессирование ХГВ не исключается и при нормальных значениях АЛТ. Исходя из этого, мы провели оценку выраженности фиброза печени с помощью транзиентной фиброэластометрии у 19 пациентов с низкой вирусной нагрузкой и уровнем АЛТ, не превышающим норму (см. таблицу).
Полученные результаты показывают, что у подавляющего большинства пациентов выраженные изменения в печени отсутствуют (F0–F1); у 1 пациента были выявлены умеренные изменения в паренхиме печени (F2) и у 4 –выраженные фибротические изменения (F3). Таким образом, у больных ХГВ при низкой вирусной нагрузке и нормальном уровне АЛТ достоверно чаще выраженные фибротические изменения в печени отсутствуют, однако прогрессирование болезни не исключается.
Выводы
- Уровень активности АЛТ остается важным лабораторным индикатором состояния функции печени и должен использоваться в процессе мониторинга пациентов с заболеваниями печени, включая ХГВ.
- Частота обнаружения высоких значений АЛТ у HBsAg-позитивных лиц отмечается чаще у мужчин и больных старше 30 лет.
- Сочетание уровня АЛТ ≥ 2 N с виремией ≥ 20 000 МЕ/мл свидетельствует об активном течении ХГВ и требует назначения этиотропной терапии.
- Нормальный уровень АЛТ и виремия < 20 000 МЕ/мл у HBsAg-положительных пациентов не исключают развития активного течения ХГВ. Таким пациентам необходимо периодически проводить углубленное обследование, чтобы исключить развитие у них фиброза печени.



