Инфекция, вызванная вирусом Эпштейна–Барр (ВЭБ), является одной из самых распространенных в мире заразных болезней. Результаты серологических исследований позволили установить, что маркеры ВЭБ присутствуют более чем у 90% взрослого населения, независимо от региона проживания. Повсеместному распространению ВЭБ в популяции человека способствует реализация практически всех известных на настоящий момент механизмов и путей передачи [1, 2]. Инфекционный процесс носит хронический характер и сопровождается сменой фаз латентного течения и реактивации. Индивидуумы с первичной и реактивацией хронической ВЭБ-инфекции являются источниками инфекции для окружающих [3–6].
С ВЭБ ассоциируют ряд патологических состояний. Более 90% случаев инфекционного мононуклеоза обусловлено данным вирусом. Он может быть причиной развития рецидивирующих инфекций верхних дыхательных путей, цитопений, гемофагоцитарного лимфогистиоцитоза, миалгического энцефаломиелита. Описано также стертое и бессимптомное течение инфекционного процесса. Кроме того, с ВЭБ-инфекцией связывают развитие аутоиммунных (ревматоидный артрит) и онкологических (лимфома Беркитта, назофарингеальная карцинома, рак желудка) болезней [7].
В большинстве стран и регионов мира случаи ВЭБ-инфекции не регистрируются. В Российской Федерации из всех клинических форм, обусловленных этим патогеном, официальному учету подлежит только инфекционный мононуклеоз, преимущественно у детей, при этом этиологическая расшифровка не проводится. Статистические сведения о случаях реактивации хронической ВЭБ-инфекции у взрослых, в том числе протекающие с выраженными клиническими проявлениями, отсутствуют [3].
На настоящий момент в мире нет зарегистрированных вакцин для профилактики ВЭБ-инфекции. В ряде государств ведутся исследования по разработке препаратов для специфической иммунопрофилактики, при успешном завершении которых ВЭБ-инфекция может перейти в разряд управляемых [8].
Это свидетельствует о наличии на современном этапе целого ряда проблем, препятствующих эффективному управлению эпидемическим процессом ВЭБ-инфекции, и требует принятия безотлагательных решений для изменения ситуации.
Успех эпидемиологического надзора кроется в понимании масштаба исследуемой проблемы. На этапе отсутствия мониторинговых наблюдений за ВЭБ-инфекцией восполнить существующие пробелы позволит математическое моделирование [9, 10]. К настоящему моменту в мире накоплен значительный опыт построения математических моделей эпидемических процессов. В отечественной эпидемиологии широко используются математические модели, построенные на основе феноменологии эпидемического процесса, которые представляют систему дифференциальных или разностных уравнений, описывающих динамику групп восприимчивых, инфицированных и выздоровевших индивидов. Наиболее распространенными из них являются компартментные модели типа SIR и SEIRF [11–15], которые успешно применяются для анализа и прогноза эпидемий гриппа, COVID-19 [16–19], лихорадки Эбола [20]. Прямая экстраполяция предложенной технологии моделирования на ВЭБ-инфекцию невозможна ввиду описанных выше особенностей эпидемического процесса и требует ее существенной корректировки.
Несмотря на масштабность проблемы ВЭБ-инфекции, в доступной литературе описана только одна модель, характеризующая эпидемический процесс этой инфекции среди населения Великобритании [21]. При этом данная модель не учитывает ряд важных эпидемиологических параметров. В частности, предполагается, что все люди рождаются здоровыми и восприимчивыми к ВЭБ и инфицируются после рождения. В то же время ряд публикаций свидетельствует о значимой доле внутриутробного инфицирования [22–26]. В этой связи предложенная зарубежными авторами модель не отражает реальной обстановки, а прогнозы на ее основе будут давать искаженное представление о перспективном развитии эпидемического процесса. Поэтому необходима разработка новой математической модели, отражающей все описанные нюансы и учитывающей особенности ВЭБ-инфекции на территории Российской Федерации.
Цель исследования – разработка математической модели эпидемического процесса ВЭБ-инфекции, составление на ее основе прогноза эффективности различных стратегий потенциальной иммунизации и определение оптимальных контингентов для вакцинации.
Материалы и методы
Для достижения поставленной цели на базе модели, предложенной Goscé L. и соавт. [21], нами разработана компартментная модель, описывающая эпидемический процесс ВЭБ-инфекции и позволяющая составить прогноз эффективности различных стратегий потенциальной иммунизации (рис. 1, см. на вклейке).
Математическое описание модели представлено системой обыкновенных линейных дифференциальных уравнений.
Изменение числа здоровых индивидуумов (восприимчивые лица):
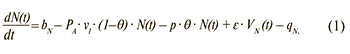
Изменение числа лиц с первичной и реактивацией хронической ВЭБ-инфекции (источники инфекции):
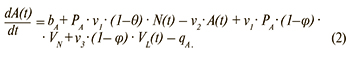
Изменение числа лиц с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией:
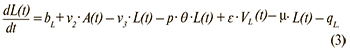
Изменение числа здоровых вакцинированных:
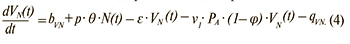
Изменение числа вакцинированных с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией:
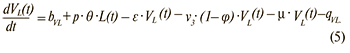
Изменение числа умерших:

Начальные условия:
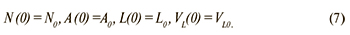
Исходными данными для моделирования явились сведения о числе лиц:
- заболевших инфекционным мононуклеозом в Российской Федерации в 2016–2020 гг. в разрезе возрастных групп (форма № 2 «Сведения об инфекционных и паразитарных болезнях», утверждена приказом Росстата от 30.12.2020 № 867);
- родившихся в Российской Федерации в 2016–2020 гг. (Российский статистический ежегодник: стат. сб./ Росстат; 2017–2021 гг.);
- умерших в Российской Федерации в 2016–2020 гг. (Российский статистический ежегодник: стат. сб./ Росстат; 2017–2021 гг.);
- родившихся с маркерами хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекции [22–26];
- живущих с маркерами хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекции в разрезе возрастных групп [27, 28].
Согласно градации по возрастам, предусмотренной формой № 2, детское население было разбито на следующие группы: дети до 1 года (группа № 1), 1–2 года (группа № 2), 3–6 лет (группа № 3), 7–14 лет (группа № 4), 15–17 лет (группа № 5). Популяция взрослых разделена на лиц в возрасте 18–39 (группа № 6) и старше 40 лет (группа № 7).
Численность возрастных групп определялась, исходя из данных о случаях инфекционного мононуклеоза и показателей заболеваемости на 100 тыс. населения в каждой из них. Полученные значения соотносились со сведениями, представленными в Российских статистических ежегодниках за исследуемый период времени.
На основе исходных данных были определены начальные значения компартментов N, A, L и D для группы № 1. В результате эпидемиологических взаимодействий с течением времени в возрастных группах соотношение здоровых и инфицированных индивидуумов изменялось по сравнению с начальными значениями. По мере достижения граничного возраста индивидуумы переходили в следующую возрастную группу уже изменившимся соотношением здоровых и инфицированных. Скорости переходов между компартментами ν1, ν2, ν3, µ и вероятность развития заболевания PA были определены, исходя из следующих предположений:
ν1 – скорость развития болезни, 1/день (скорость перехода из «N» в «A»), рассчитывается из предположения, что средняя длительность инкубационного периода составляет 42 дня [29], = 0,0238 (1/день);
ν2 – скорость выздоровления, 1/день (скорость перехода из A в L), рассчитывается из предположения, что средняя длительность заболевания составляет 90 дней [30], = 0,0111 1/день;
ν3 – скорость реактивации, 1/день (скорость перехода из L в A), принята равной нулю для возрастных групп № 1 (дети до 1 года) и № 2 (дети 1–2 года), для других возрастных групп значение подбирается в процессе моделирования;
µ – скорость перехода индивидуумов в категорию умерших, 1/день, значение µ для каждой возрастной группы подбирается в процессе моделирования;
PA – вероятность развития заболевания вследствие контакта между здоровыми и лицами с первичной и реактивацией хронической ВЭБ-инфекции, значение параметра подбирается в процессе моделирования.
Подбор значений описанных параметров и оценку адекватности расчетных данных проводили путем их сопоставления с официальными статистическими показателями заболеваемости, рождаемости и смертности, а также с результатами ранее проведенных исследований [22–28].
После того как был составлен прогноз развития эпидемической ситуации на современном этапе, проведена аналогичная оценка при введении потенциальной вакцинации, для которой были выбраны следующие условия:
- эффективность гипотетической вакцины 90%;
- охват вакцинацией составляет 95% индивидуумов декретированной группы;
- период формирования протективной защиты 1 месяц (30 дней);
- продолжительность протективной защиты 10 лет.
Исходный выбор групп для потенциальной вакцинации основывался на данных о распространенности (превалентности) ВЭБ, которая была минимальной среди детей до 1 года [27, 28]. В то же время возможность внутриутробного инфицирования [22–26] определяет дополнительную необходимость формирования специфической защиты у женщин детородного возраста (18–39 лет). Сопоставление с другими инфекциями (корь, краснуха), управляемыми средствами специфической профилактики, иммунизация против которых включена в национальный календарь профилактических прививок, позволяет рассматривать женщин 18–39 лет в качестве дополнительного декретированного контингента для вакцинации против ВЭБ [31]. Для проверки выдвинутой гипотезы были рассмотрены стратегии, включающие следующие контингенты:
- здоровые дети до 1 года;
- здоровые женщины 18–39 лет;
- здоровые дети до 1 года и женщины 18–39 лет;
- дети до 1 года (здоровые и с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией);
- женщины 18–39 лет (здоровые и с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией);
- дети до 1 года и женщины 18–39 лет (здоровые и с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией).
Под термином «здоровые» подразумеваются неинфицированные ВЭБ индивидуумы, которые после проведенной вакцинации являются невосприимчивыми к данному вирусу на протяжении 10 лет. Иммунизация лиц с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией подразумевает формирование у индивидуумов протективной защиты, предотвращающей реактивацию в течение 10 лет.
Скорость перехода индивидуумов после вакцинации в компартмент V (VL и VN) рассчитана по формуле:

где 30 – число дней, в течение которых формируется протективная защита [32].
По истечении указанного срока вакцинированные лица со скоростью ε возвращаются в компартменты N или L. Скорость ε определена из предполагаемой длительности защитного действия вакцины
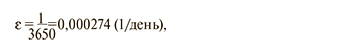
где 3650 – это 10 лет × 365 дней.
Окончательный выбор оптимальных декретированных групп для проведения потенциальной вакцинации был сделан по результатам математического моделирования с позиции прогноза эффективности влияния на эпидемической процесс.
Расчеты проведены в системе компьютерной математики Mathcad 15/MathcadPrime 1.0. [33]. Результаты моделирования представлены в графическом виде.
Результаты
В период 2016–2020 гг., статистические сведения за который легли в основу разработанной модели, в Российской Федерации показатели заболеваемости инфекционным мононуклеозом были максимальными в 2019 г. Спад заболеваемости в 2020 г. совпал с эпидемическим распространением в стране SARS-Cov-2 и обусловлен, вероятно, двумя причинами – разобщением населения в результате проводимых противоэпидемических мероприятий и низким уровнем регистрации ввиду изменившихся приоритетов.
В структуре заболевших преобладали лица в возрасте до 18 лет – 83,7%. Удельный вес взрослого населения среди всех заболевших инфекционным мононуклеозом составил 16,3%. При этом наиболее высокие средние показатели заболеваемости зарегистрированы в возрастных группах 1–2 года (146,5 на 100 тыс. населения) и 3–6 лет (124,8 на 100 тыс. населения).
Сопоставление средних показателей регистрируемой заболеваемости инфекционным мононуклеозом в разных возрастных группах с прогнозными значениями, полученными в результате математического моделирования, а также рождаемости и смертности выявило наличие прямых сильных значимых корреляционных связей (коэффициент ранговой корреляции Спирмена pз = 1, Ткр.= 0; pр = 1, Ткр.= 0; pс = 1, Ткр.= 0 соответственно), что свидетельствует об адекватности разработанной модели и возможности ее использования для анализа и прогноза параметров эпидемического процесса ВЭБ-инфекции.
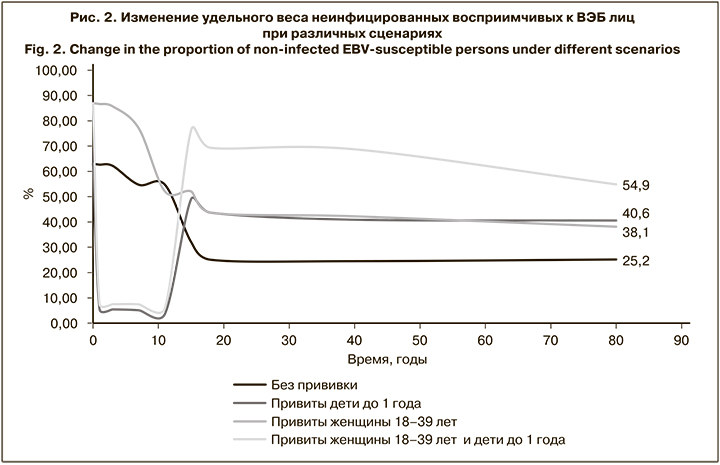
Результаты моделирования показали, что доля здоровых восприимчивых к данному возбудителю лиц при рождении составляет 63% и сохраняется на этом уровне в течение первого года жизни. Постепенно, вследствие контактов с источниками инфекции восприимчивые лица вовлекаются в эпидемический процесс, их удельный вес сокращается и во взрослой популяции не превышает 25% (рис. 2). При этом пропорционально увеличивается доля лиц с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией с 37% при рождении до 75% в возрастной группе старше 18 лет (рис. 2).
Изменение сложившейся эпидемической ситуации представляется возможным путем сокращения доли восприимчивого контингента до того, как указанные лица будут инфицированы. Кроме того, важным аспектом является снижение удельного веса индивидуумов с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией, которые в периоды реактивации становятся источниками инфекции, либо создание условий, препятствующих реактивации. Достижение поставленных задач возможно за счет введения потенциальной массовой вакцинации.
Моделирование различных стратегий иммунизации показало, что при использовании в качестве декретированного контингента только здоровых индивидуумов из группы № 1 к концу первого года жизни защиту от инфицирования ВЭБ приобретают 57,5% индивидуумов, а доля восприимчивых лиц снижается с 63% при рождении до 5,5%. На этом фоне происходит выраженное (в 6,8 раза) снижение числа детей с инфекционным мононуклеозом. Число лиц с хронической латентной инфекцией практически не изменяется. Сокращение доли восприимчивых лиц способствует снижению заболеваемости в более старших возрастных группах на протяжении последующих 10 лет (предполагаемый срок поствакцинальной защиты). Однако наличие большого пула детей с латентной инфекцией (около 37% при рождении) определяет возможность ее последующей реактивации с вовлечением в эпидемический процесс незащищенной когорты.
При иммунизации здоровых женщин 18–39 лет доля защищенных лиц составит всего 27,8%, чего явно недостаточно для создания надлежащей иммунной прослойки. Кроме того, по аналогии с первой стратегией, число индивидуумов с латентной инфекцией не изменится. Исходя из этого, в период беременности у 67,25% женщин может произойти реактивация хронической ВЭБ-инфекции, что будет способствовать внутриутробному инфицированию.
Таким образом, обе описанные стратегии показали свою несостоятельность из-за невозможности значимого сокращения удельного веса лиц с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией.
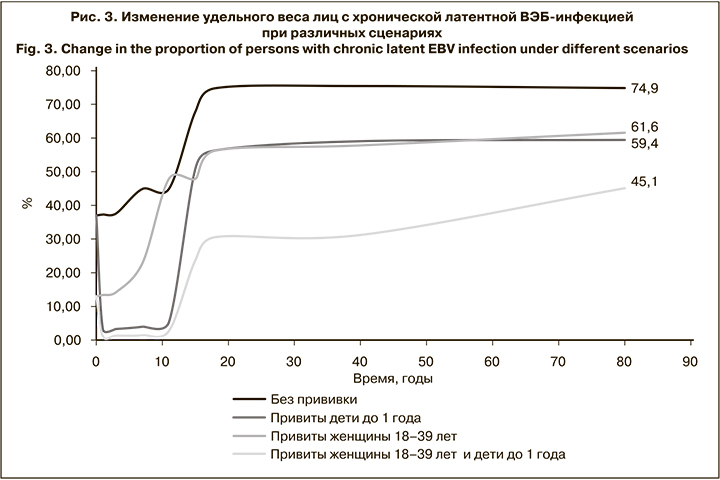
Проведение вакцинации всех детей в возрасте до 1 года (здоровых и с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией) позволит к 18 годам повысить долю не вовлеченных в эпидемический процесс индивидуумов до 43,7% по сравнению с 25,1% при отсутствии мер противодействия. Через 80 лет от момента начала прививочной кампании данный показатель составит 40,6% против 25,2% соответственно (рис. 3). При этом доля лиц с хронической латентной инфекцией существенно сократится по сравнению с периодом, когда вакцинация не применяется, и к 18 годам составит 56,3% против 74,8%, к 80 – 59,4% против 74,9% соответственно (рис. 2).
Исходя из заданных условий моделирования, вакцинация женщин 18–39 лет (здоровых и с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией) позволяет предотвратить развитие первичной и реактивации хронической ВЭБ-инфекции в период беременности. Следовательно, дети от вакцинированных матерей будут рождаться здоровыми. Таким образом, удельный вес здоровых новорожденных при использовании данной стратегии вакцинации составит 86,9%. С течением времени доля здоровых индивидуумов сократится (к 18 годам до 43,7%, к 80 – до 38,1%), однако на протяжении всего периода наблюдения будет выше, чем при отсутствии мер противодействия (25,1 и 25,2% соответственно; рис. 2). Доля лиц с хронической латентной инфекцией будет сопоставима с таковой при вакцинации детей до 1 года и составит к 18 годам 56,2%, к 80 – 61,6%.
Наиболее эффективной оказалась стратегия комбинированной вакцинации, когда прививкам одновременно подлежат как дети до 1 года, так и женщины 18–39 лет (здоровые и с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией). Такой подход потенциально позволит повысить удельный вес не вовлеченных в эпидемический процесс лиц до 69,4% к 18 годам с незначительным снижением к 80 годам до 54,9%. На этом фоне доля индивидуумов с латентной хронической ВЭБ-инфекцией к 18 годам составит всего 30,6% по сравнению с 74,8% при отсутствии мер противодействия. При использовании данной стратегии вакцинации аналогичные показатели в 80 лет также будут существенно ниже, чем при отсутствии иммунопрофилактики – 45,1 и 74,9% соответственно (рис. 3).
Увеличение доли восприимчивого контингента при наличии достаточного числа источников инфекции, как правило, способствует росту заболеваемости. По результатам моделирования установлено, что прогнозная заболеваемость совокупного населения при использовании каждой из трех выбранных стратегий вакцинации будет несколько выше аналогичного показателя для популяции, в которой иммунизация не проводилась. При вакцинации как здоровых, так и лиц с хронической латентной инфекцией фактором, сдерживающим рост заболеваемости, будет являться сокращение распространенности возбудителя в популяции и, как следствие, снижение числа источников инфекции из числа индивидуумов с реактивацией ВЭБ-инфекции.
Кроме того, использование разных стратегий вакцинации будет способствовать изменению показателей заболеваемости в отдельных возрастных группах. Так, при иммунизации детей до 1 года основными группами риска инфицирования будут являться дети 7–14 и 15–17 лет, в то время как при отсутствии прививок максимальные показатели имеют место среди детей 1–2 и 3–6 лет. В случае если прививкам будут подлежать женщины 18–39 лет, можно ожидать роста заболеваемости практически во всех возрастных группах за счет существенного увеличения когорты восприимчивых лиц. При иммунизации одновременно женщин 18–39 лет и детей до 1 года пик заболеваемости придется на возраст 15–17 лет, а показатели в более старших группах населения будут сопоставимы с таковыми у детей.
Обсуждение
Снижение бремени заразных болезней входит в перечень приоритетных задач органов здравоохранения большинства мировых держав. Управление эпидемическим процессом широко распространенных в человеческой популяции инфекций позволяет оказывать влияние на демографические показатели, такие как смертность и средняя продолжительность жизни [31, 34]. В настоящий момент ВЭБ-инфекция относится к разряду неуправляемых и не подлежит эпидемиологическому контролю ввиду отсутствия действенных мер профилактики, а погрешности статистического учета не позволяют адекватно оценить ситуацию. В связи с этим разработка математической модели, позволяющей оценить масштаб проблемы и составить объективный прогноз, является своевременной и необходимой мерой эпидемиологического реагирования.
До проведения настоящего исследования попытки моделирования эпидемического процесса ВЭБ-инфекции в Российской Федерации не предпринимались, а единственная модель, разработанная за рубежом [21], не учитывает значимой когорты новорожденных, инфицированных внутриутробно. Отечественные и зарубежные исследования показали, что около 37% детей к моменту рождения уже инфицированы ВЭБ [22–26]. Данный аспект был учтен при разработке описанной нами модели. Это позволило создать объективные условия для моделирования, адекватность которого доказана путем сопоставления полученных параметров с демографическими показателями и данными по заболеваемости и распространенности ВЭБ-инфекции.
Важным преимуществом предложенной модели является возможность прогнозирования эпидемической ситуации как при отсутствии мер специфической профилактики, так и при ее применении. В настоящем исследовании описано использование гипотетической вакцины, обладающей заданными характеристиками, в то время как реально разработанные препараты могут иметь отличные параметры эффективности. Кроме того, к моменту регистрации вакцин эпидемическая ситуация по ВЭБ-инфекции может измениться. К переменным значениям относится и параметр охвата населения вакцинацией. При разработке настоящей модели все описанные нюансы были учтены.
Предложенная модель позволяет решить еще одну очень важную задачу – определить оптимальный декретированный контингент для проведения специфической иммунопрофилактики. Стратегия вакцинации только здоровых индивидуумов, предложенная исследователями из Великобритании [21], обнаружила свою несостоятельность ввиду незначительного удельного веса данной когорты, что не позволяет создать достаточную иммунную прослойку в популяции. Результаты моделирования показали, что наиболее оптимистичного прогноза можно добиться благодаря введению комплексной вакцинации здоровых и лиц с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией в возрасте до 1 года и женщин 18–39 лет. Такой подход при заданных условиях позволит более чем в 2 раза снизить бремя ВЭБ-инфекции уже через 20 лет от начала иммунизации и сохранить достигнутый результат спустя 80 лет.
В то же время это приведет к существенным изменениям возраста, в котором индивидуумы будут переносить первичную ВЭБ-инфекцию [35]. При вакцинации детей до 1 года и женщин 18–39 лет самой незащищенной когортой станут подростки 15–17 лет. Действие иммунной защиты после гипотетической вакцинации к этому моменту закончится и накопится большой пул восприимчивых лиц, который при наличии достаточного числа источников инфекции составит группу риска первичного инфицирования ВЭБ. Для решения данной проблемы можно использовать опыт профилактики иных инфекций, где снижение заболеваемости в конкретных возрастных группах достигается путем введения дополнительных ревакцинаций [36]. Кроме того, описанный аспект необходимо учесть в ходе разработки и проведения клинических исследований кандидатных вакцин для профилактики ВЭБ-инфекции с целью выбора оптимальной схемы специфической профилактики.
Выводы:
Предложенная компартментная модель учитывает все известные в настоящий момент особенности ВЭБ-инфекции, является адекватной и надежной, что подтверждается наличием значимых прямых сильных корреляционных связей между прогнозными параметрами и официальными статистическими показателями заболеваемости, рождаемости и смертности от инфекционного мононуклеоза.
Результаты моделирования показали, что на современном этапе распространенность ВЭБ в популяции изменяется в зависимости от возраста и является минимальной в группе детей до 1 года (37,3%), максимальной – среди лиц 18 лет и старше (75%). Рост показателя сопровождается пропорциональным снижением удельного веса восприимчивых к ВЭБ индивидуумов с 62,7 до 25% соответственно.
Проведение потенциальной вакцинации в рамках предложенных стратегий позволит в течение последующих 80 лет снизить распространенность ВЭБ среди населения, но не элиминировать возбудителя.
Анализ прогноза эффективности выбранных стратегий потенциальной вакцинации показал, что оптимальными декретированными контингентами являются здоровые индивидуумы и лица с хронической латентной ВЭБ-инфекцией обоего пола в возрасте до 1 года и женщины 18–39 лет. Иммунизация указанных групп в рамках выбранных в ходе моделирования параметров позволит повысить удельный вес не вовлеченных в эпидемический процесс лиц до 69,4% к 18 годам с незначительным снижением до 54,9% к 80 годам. Распространенность ВЭБ в популяции к 18 годам сократится в 2,5 раза и составит 30,6%, к 80 – в 1,7 раза (45,1%).
Предложенная математическая модель может быть легко адаптирована под параметры любой вакцины для профилактики ВЭБ-инфекции после ее разработки и регистрации и позволяет в короткие сроки выбрать наиболее эффективную стратегию проведения иммунизации. В качестве дополнительных мер воздействия на эпидемический процесс ВЭБ-инфекции в прогнозируемом будущем можно рассматривать введение ревакцинации с интервалом, соответствующим продолжительности протективного действия конкретной вакцины.



