Острые кишечные инфекции (ОКИ) продолжают занимать ведущее место в инфекционной патологии детского возраста, уступая по массовости и экономическому ущербу только острым респираторным заболеваниям и гриппу [1, 2]. В этиологической структуре ОКИ в настоящее время в нашей стране, как и во всем мире, выделяются вирусные диареи, однако из бактериальных инфекций за последние годы на первое место вышли сальмонеллезы, заболеваемость которыми, по данным официальной статистики за 2017 г., превышает заболеваемость шигеллезами в 4,9 раза: 22,07 против 4,54 на 100 тыс. населения соответственно [3]. Показатель заболеваемости детей до 14 лет в 2017 г. был выше общепопуляционного в 2,7 раза (62,33 против 22,07), его максимальное значение отмечено в возрастной группе 1–2 лет (119,6 на 100 тыс. детей данного возраста). За последние 40 лет произошла эволюция клинико-эпидемиологических закономерностей сальмонеллезов у детей1, что обусловлено сменой доминирующего серовара с S. Typhimurium на S. Enteritidis, а в связи с этим – и контингента заболевших (преобладание детей 1–7 лет, не организованных в детские коллективы), и путей инфицирования (преимущественно пищевой в семейных очагах) [4–6]. Одной из важных проблем современных сальмонеллезов у детей является постинфекционное бактерионосительство, особенно длительное (свыше 1,5 мес.).
Бактерионосительство – это распространенная форма функционирования биологической системы «паразит–хозяин», одна из природных иллюстраций закона единства и борьбы противоположностей, где параллельная эволюция хозяина и паразита – основной инструмент совершенствования самой системы [7, 8]. Это своеобразная форма симбиоза патогенных микроорганизмов и организма хозяина, приводящая к длительному персистированию возбудителя без клинических проявлений болезни, которая имеет большую эпидемиологическую значимость: способствует сохранению возбудителя в межэпидемический период и является дополнительным механизмом развития эпидемического процесса в связи с возможностью трансформирования его в манифестную форму болезни под влиянием разных факторов [9, 10]. Например, отмечено, что операции на открытом сердце у бактерионосителей – детей младшего возраста могут приводить к сальмонеллезной септицемии [11]. Обследование, тем более повторного, всех детей после перенесенной инфекции в стационарах, как правило, не проводится, а в амбулаторных условиях оно не предусмотрено существующими нормативными документами2, что приводит к недовыявлению постинфекционного бактерионосительства со всеми вытекающими последствиями.
Поэтому изучение истинной частоты и особенно длительности постинфекционного выделения сальмонелл имеет не только эпидемиологическое, но и социальное значение. Сведения об этом в доступной литературе, как зарубежной, так и отечественной, весьма немногочисленны, противоречивы и зависят от возраста пациентов. Так, по данным зарубежных исследователей, через 5 мес. после постановки диагноза «сальмонеллез» 4% детей младше 6 мес. продолжали выделять сальмонеллы, а через год после перенесенного сальмонеллеза выделение возбудителя сохраняется у 2,6% детей младше 5 лет и менее чем у 1% детей старше 5 лет и взрослых [12, 13]. Однако в зарубежной литературе имеются и единичные работы, свидетельствующие о большей частоте длительного бактериовыделения сальмонелл – от 25 до 65% [14–16], в том числе, до 32% у детей первого года жизни [17, 18]. Так, у 60% детей в возрасте младше 5 лет обнаружено выделение сальмонелл через 20 нед. после клинического выздоровления, а около 5% детей продолжали выделять этот микроорганизм и через год [19, 20].
Данные отечественных авторов о частоте длительного бактериовыделения после перенесенного сальмонеллеза у детей еще более разноречивы – от 0,1 до 44,1% [8, 21–24 ], что связано по-видимому, с разной кратностью контрольного бактериологического обследования. При этом установлено влияние на частоту и длительность постинфекционного бактериовыделения не столько вида, сколько антибиотикорезистентности возбудителя. Так, в 60–70- е годы XX века частота выделения свыше 3 нед. S. Typhimurium чувствительных и резистентных к антибиотикам, составляла 4,7 и 13,4% соответственно3, а в начале XXI века при госпитальном сальмонеллезе S. Typhimurium регистрировали у 41,7% больных, в том числе свыше 3 мес. – у 12,5% [22, 25]. Но и в современных условиях при сальмонеллезе, вызванном S. Typhimurium, все еще доминирующем в южных регионах страны, повторное бактериовыделение, по данным Л.У. Улухановой, выявляется у половины детей раннего возраста после купирования клинических проявлений болезни и сохраняется до 1,5 мес. и более у 1/3 из них4.
При сальмонеллезе, вызванном S. Enteritidis, также чаще выявляют повторное бактериовыделение резистентных, чем чувствительных к антибиотикам штаммов – в 33,3 и 13,0% случаев соответственно1, что подтверждают и работы других авторов [25]. В наших предыдущих исследованиях5 было показано, что реконвалесцентное бактерионосительство наблюдалось в годы преобладания резистентных штаммов чаще, чем в годы преобладания чувствительных (2/3 и 1/3 соответственно). При этом при повторном обследовании детей, выписанных из стационара, оказалось, что у 20% из них продолжают высеваться сальмонеллы в течение 1,5 мес. и дольше и значительно чаще (42,1%) – при неадекватном лечении (повторные курсы антибиотиков) [23]. К таким же выводам пришли и другие авторы, показавшие, что период бактериовыделения может увеличиваться из-за неадекватного применения антибиотиков [25–27]. Так, М.К. Бехтерева и соавт. [25] отмечают, что реконвалесцентное бактериовыделение Salmonella spp. зарегистрировано у 47,9% детей, получавших антибактериальную терапию. При этом S. Enteritidis была выделена в 79,6% случаев.
Установлено, что в формировании постинфекционного бактерионосительства играют роль особенности макроорганизма (генетическая предрасположенность, состояние желчного пузыря), свойства возбудителя (антибактериальная резистентность, антилизоцимная активность, способность разрушать комплемент), а также особенности взаимодействия сальмонелл с клетками иммунной системы, приводящие к их персистированию в эпителиоцитах.
Известно, что аномалии и заболевания желчного пузыря, приводящие к застою желчи, способствуют формированию длительного бактерионосительства, поскольку сальмонеллы проникают в желчный пузырь, а желчь является хорошей питательной средой для них [6, 28]. В эксперименте было установлено, что сальмонеллы способны не только сохраняться в эпителии желчного пузыря [29], но и формировать биопленки – патогенетический фактор хронизации инфекционных процессов, поскольку интеграция бактерий в сообщество обеспечивает им большую устойчивость к воздействию факторов внешней среды, включая антибактериальные препараты [30, 31]. Более того, формирование сальмонеллами биопленки и их взаимодействие с корпускулярными компонентами желчи приводят к дисбалансу ее коллоидного равновесия, что может привести к образованию желчных камней [29, 32].
Формированию реконвалесцентного бактерионосительства способствует и нарушение микробиоценоза кишечника [33].
В лабораторных исследованиях на мышах были получены данные о том, что при наличии антигена гистосовместимости HLA-B27 снижается синтез NO клетками, что способствует персистированию сальмонелл (S. Enteritidis) [34]. Установлено также, что наличие антигена HLA-B27 не только может сделать людей более восприимчивыми к сальмонеллезной инфекции [35], но и способствует персистированию сальмонелл [34].
Присутствие антигена А19 также обусловливает риск формирования длительного реконвалесцентного бактерионосительства S. Enteritidis и S. Typhimurium у детей [36].
Важнейшим свойством сальмонелл является их антилизоцимная активность. Экспериментальным путем на животных, культуре ткани и методом популяционного анализа доказано, что антилизоцимный признак можно рассматривать как маркер персистенции бактерий, способных к внутриклеточному паразитированию. Для персистирования бактерий имеет значение и их липополисахаридный профиль. Установлено, что О-антиген S. Minnesota напрямую разрушал действие комплемента, мешая прилипанию мембраноатакующего комплекса (С5в- 9) в критических участках бактериальной стенки [7].
Эксперименты in vitro и in vivo показали, что S. Typhimurium способны не только выживать внутри кишечного эпителия [37], но и перемещаться из инфицированных в неинфицированные эпителиальные клетки с помощью эффекторного белка PipB2 [38]. Установлено, что сальмонеллы могут не только разрушать макрофаги, но и размножаться внутри них и сохраняются в фагосоме, где формируют устойчивую вакуоль с мембраной в непосредственной близости к бактерии. Это увеличивает сопротивление антибактериальным пептидам и окислительному стрессу, а изменение фагосомы увеличивает внутриклеточное выживание и уменьшает распознавание сальмонелл компонентами врожденного иммунитета [39].
Установлено, что санация от сальмонелл осуществляется при участии NK-клеток, продуцирующих IFN-γ; Т-хелперов 1-го типа, продуцирующих IL-2; макрофагов, продуцирующих IL-15; инфицированных сальмонеллами макрофагов, секретирующих IL-12, IL-18 [40].
Сальмонеллы также способны снижать иммунный ответ человека, нарушая функции дендритных и Т-клеток [41].
В формировании реконвалесцентного бактерионосительства имеет место нарушение регуляции локального иммунного ответа и дефицит местного иммунитета, о чем свидетельствует низкое содержание секреторного IgA (sIgA), свободного секреторного компонента (SC), антител к О-антигену сальмонелл, лактоферрина, лизоцима, определяемых в слюне и копрофильтратах; низкий уровень цитокинов IL-1Ra (антагониста IL-1) и IL-4 в копрофильтратах и, напротив, высокий уровень IgM, IgG (за счет IgG1 и IgG4) цитокинов IL-6, IL-8, IL-4, IFN-ɣ [33, 42]. Однако в этих работах возрастные особенности иммунного ответа при длительном бактерионосительстве сальмонелл не освещены.
В доступной литературе имеются лишь единичные работы, посвященные изучению иммунного ответа у детей с длительным бактериовыдением сальмонелл6. У них установлено нарушение всех звеньев иммунного ответа: фагоцитоза (снижение ХИ), гуморального звена (сочетанное снижение уровней IgG и IgM), субпопуляций лимфоцитов (снижение количества CD4+-лимфоцитов и иммуннорегуляторного индекса) и особенно – подавление миграции лейкоцитов в РТМЛ (при специфической и неспецифической стимуляции) [23].
Нерешенными остаются и вопросы терапии детей с длительным бактериовыделением, поскольку общепринятые методы (повторные курсы антибиотиков) не только недостаточно эффективны, но и способствуют увеличению сроков санации от возбудителя [6, 23, 25–27]. Поэтому представляется неубедительной рекомендация Е.В. Коцарь и соавт. [43], предложивших лечить сальмонеллезных бактерионосителей (без указания возраста) антибиотиками только на основании высокой чувствительности к ним 20 изученных штаммов возбудителя (без указания сероваров и без представления результатов лечения).
Бактерионосителям в качестве этиотропных средств назначают специфические бактериофаги [6, 21, 28, 44], однако они высокоэффективны, особенно при сочетании с желчегонными средствами, только в острую фазу болезни: их санирующая эффективность у детей может достигать 72–98% [28], а у взрослых в очагах госпитального сальмонеллеза они позволяют сократить частоту бактерионосительства сальмонелл в 6–20 раз [45]. Однако при длительном бактерионосительстве бактериофаги, как и антибиотики, малоэффективны [23].
Учитывая сказанное выше, наиболее целесообразно назначение этим больным иммунокорригирующих препаратов. Однако данные об этом виде терапии весьма немногочисленны и касаются, преимущественно, лечения в острой фазе болезни и в период ранней реконвалесценции.
Результаты проведенных нами исследований показали эффективность КИП – отечественного энтерального комплексного иммунноглобулинового препарата, содержащего IgG, IgM, IgA и специфические антитела к энтеробактериям, в том числе сальмонеллам, и способного блокировать рецепторы микробных клеток, предотвращая их адгезию и размножение в эпителиоцитах. Санирующий эффект при бактериовыделении S. Typhimurium в период реконвалесценции был достигнут у 85% детей против 55,2% в контрольной группе7. Установлено также, что включение кипферона в комплексную терапию сальмонеллеза, вызванного S. Typhimurium, в острую фазу болезни позволило увеличить долю детей с санацией от возбудителя с 50 до 71%, что сопровождалось и нормализацией параметров иммунного гомеостаза [46].
Имеются единичные данные о санирующей эффективности включения в терапию взрослых сальмонеллезных реконвалесцентных бактерионосителей (S. Enteritidis), наряду с пробиотиками и витаминами, полиоксидония – активного высокомолекулярного соединения с выраженной иммуномодулирующей активностью [33, 47]. Было установлено сокращение в 1,5 раза сроков бактериовыделения и ускорение нормализации микробиоценоза толстой кишки; стимулирующее влияние на показатели местного иммунитета (sIgA, SC, общий IgA, лизоцим, титры специфических антител к О-антигену сальмонелл); увеличение количества отдельных субпопуляций лимфоцитов (CD16, CD56, CD95) и изменение содержания цитокинов с восстановлением баланса Th1- и Th2-цитокинов, а также функциональной активности нейтрофилов. В условиях in vitro выявлено подавление полиоксидонием антикомплементарной активности сальмонелл [33, 47].
В нескольких опубликованных работах подтверждена эффективность включения в терапию сальмонеллезов у детей циклоферона – низкомолекулярного индуктора IFN-α и IFN-γ, которые обладают не только иммуномодулирующим и противовоспалительным действием, но и подавляют факторы персистенции грамотрицательных микроорганизмов, в том числе сальмонелл (их антилизоцимную и антикомплементарную активность) [48, 49]. Установлено, что циклоферон способствует более редкому формированию реконвалесцентного бактерионосительства сальмонелл [50] и освобождению от возбудителя у 95% получавших его пациентов [51].
Однако данных о применении вышеописанных препаратов (КИП, кипферона, полиоксидония, циклоферона) при длительном реконвалесцентном бактерионосительстве сальмонелл нет, а критерии истинного выздоровления авторами не указаны.
Из многочисленных существующих на отечественном фармацевтическом рынке иммуномодуляторов наиболее перспективными являются бактериальные лизаты – иммуномодуляторы микробного происхождения, поскольку именно нормальная микрофлора определяет становление, развитие и поддержание иммунитета человека, а среди них – наиболее очищенного полусинтетического отечественного препарата ликопид. В его основе минимальный биологически активный фрагмент пептидогликана клеточной стенки всех известных бактерий с хорошо изученным механизмом действия (активация всех звеньев иммунного ответа через макрофагально-моноцитарную систему, как это происходит в естественных условиях) [52]. Препарат разрешен к применению у детей с 1996 г. и успешно применяется для лечения самых разных инфекций: ОРВИ у часто болеющих детей [53], герпетических инфекций у детей раннего возраста [54], а также для санации от микобактерий туберкулеза [55] и Helicobacter pylory [56] у взрослых и условно-патогенных микроорганизмов и Candida albicans [57] – у детей.
В исследовании Л.У. Улухановой ликопид был использован в составе комплексной терапии в острой фазе сальмонеллеза, вызванного S. Typhimurium8. Санирующий эффект получен у 81% детей, а при последовательном применении после кипферона – у 90% детей (против 50% больных, не получавших иммунопрепаратов).
Имеется лишь одно исследование, в котором применен ликопид для лечения детей с длительным постинфекционным сальмонеллезным бактерионосительством, у которых предыдущее лечение антибиотиками, бактериофагами и КИП оказалось неэффективным [23, 58]. Изучена санирующая эффективность ликопида у 28 детей, перенесших сальмонеллез и продолжавших выделять сальмонеллы после курса комплексной терапии при отсутствии дисфункций со стороны желудочно-кишечного тракта. Длительность бактериовыделения к моменту начала терапии ликопидом у большинства детей составляла 1,5 мес. и более, в том числе почти у половины – более 3 мес. Дети получали 3 курса препарата по 1 мг 1 раз в день под язык в течение 10 дней с перерывом в 20 дней. Освободились от возбудителя 96,4%, при этом критерии выздоровления были жесткими: 3 отрицательных результата бактериологического посева, взятых подряд, и 4-й – через месяц. Освобождение от возбудителя сопровождалось увеличением фагоцитарного индекса нейтрофилов и моноцитов, повышением иммунорегуляторного индекса и показателей миграции лейкоцитов в реакции торможения миграции лейкоцитов (РТМЛ).
Поскольку длительное (свыше 1,5 мес.) постинфекционное бактериовыделение сальмонелл у детей достаточно распространено, но недовыявляется, имеет не только эпидемиологическую, но и социальную значимость (особенно для детей, посещающих детские дошкольные учреждения, и их родителей), а терапия представляет значительные трудности и требует длительного времени, еще более важной проблемой является его прогнозирование и профилактика. Однако сведений по этому вопросу очень мало.
Так, О.В. Бухарин и соавт.9, проанализировав известные ранее способы прогнозирования длительного бактериовыделения сальмонелл у взрослых, показали их недостатки. Показатели, выявляющие снижение иммунологической защиты в острую фазу болезни [уровень свободных и связанных в иммунные комплексы копроантител в РНГА (реакции непрямой гемагглютинации); уровень циркулирующих лимфоцитов, сенсибилизированых к сальмонеллезному О-антигену в реакции антигенспецифического розеткообразования; снижение индекса завершенного фагоцитоза, индекса литической активности сыворотки крови, мононуклеарного индекса; недостаточное нарастание специфических антител] учитывают биологические свойства сальмонелл не полностью. Кроме того, информативность этих показателей выявляется только на 3–4-й неделе заболевания.
Недостаток метода определения антилизоцимной активности чистой культуры сальмонелл, выделенной от больного, связан с тем, что гидролитическое расщепление лизоцимом пептидогликанового слоя клеточной стенки характерно преимущественно для грамположительных бактерий и менее – для грамотрицательных, в том числе сальмонелл. Авторы предложили метод прогнозирования реконвалесцентного бактерионосительства сальмонелл путем определения уровня лактоферрина в копрофильтратах и антилактоферриновой активности сальмонелл10. Лактоферрин – неспецифический клеточный протектор на поверхности кишечного эпителия и фаголизомах нейтрофильных гранул – оказывает бактериостатическое действие. Кроме того, косвенно, с помощью потенцированного действия лактоферрина, сальмонеллы с высокой антилизоцимной активностью способны инактивировать и большое количество лизоцима в клетках и тканях. Пациенты, у которых в острую фазу болезни выявляли дефицит лактоферрина в копрофильтратах (460–1400 нг/мл) и высокую антилактоферриновую активность сальмонелл (7,8–13,0 нг), являются группой риска реконвалесцентного бактерионосительства. Авторы показали эффективность метода у 93,8% взрослых, больных сальмонеллезом. Уровень лактоферрина в копрофильтрате у реконвалесцентных бактерионосителей по сравнению с другими пациентами был ниже в 2,3 раза в период разгара болезни и в 3,7 раза – в период реконвалесценции 9,11.
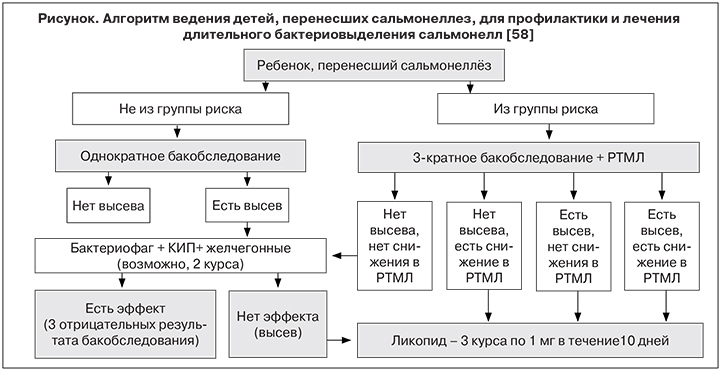
В работе Л.Н. Милютиной и соавт. [58] впервые предложен алгоритм ведения детей после перенесенной сальмонеллезной инфекции для своевременного прогнозирования, диагностики, профилактики и лечения реконвалесцентного бактерионосительства сальмонелл (см. рисунок) и дифференцированный подход к количеству обследований таких детей на сальмонеллез. Детям, отнесенным к группе риска по затягиванию санации от возбудителя (с заболеваниями, вызванными полирезистентным к антибиотикам штаммами сальмонелл; с сочетанным течением сальмонеллеза с вирусными и другими инфекциями; с множественными отягощающими факторами в анамнезе, в том числе, избыточно лечившимся антибиотиками) рекомендуется не однократное, а 3-кратное бактериологическое обследование после клинического выздоровления (учитывая дискретность выделения возбудителя) и проведение 1 иммунологического теста (РТМЛ). При положительных результатах обоих или одного из этих методов обследования рекомендуется проведение иммунной терапии ликопидом (тремя курсами). Детям, не отнесенным к группе риска, достаточно 1 бактериологического обследования, а при наличии положительного результата – 1–2 курсов лечения по схеме: бактериофаг + КИП + желчегонные препараты и только при отсутствии эффекта рекомендуются 3 курса иммунотерапии. Однако данных о результатах практического применения этого алгоритма пока нет.
Заключение
Постинфекционное бактерионосительство сальмонелл – достаточно распространенное явление, которое имеет эпидемиологическую и социальную значимость, особенно у детей, но недовыявляемое; методы лечения, используемые в широкой практике, неэффективны, а прогнозирование и иммунопрофилактика реконвалесцентного носительства, особенно длительного, недостаточно разработаны, не внедрены в практику. В связи с этим целесообразно продолжать исследования в этом направлении, а также широко применять уже разработанные критерии прогнозирования для накопления опыта ранней профилактики длительного постинфекционного бактерионосительства сальмонелл, прежде всего у детей.



