Клиническая трансплантология – интенсивно развивающаяся область медицинской науки и технологий, позволяющая успешно использовать трансплантацию органов как метод лечения различных заболеваний, не поддающихся традиционным методам. Клиническая трансплантология решает задачи не только спасения неизлечимых больных, но и достижения длительного выживания пациентов, их медицинской и социальной реабилитации. Свидетельством успехов трансплантологии является быстрое увеличение числа новых центров, клиник и отделений трансплантации как за рубежом, так и в нашей стране. В Российской Федерации в 2015 г. выполнено 1485 операций по трансплантации органов [1].
В области трансплантологии, как и в других направлениях клинической медицины, имеются серьезные проблемы. Одна из них – инфекционные осложнения, которые могут развиваться после трансплантации органов. Возбудителями инфекции являются бактерии, вирусы, грибы. Часто этому способствуют имеющиеся у пациентов очаги хронической и латентной инфекции, в том числе микоплазменной. Возбудители заболевания – микоплазмы – относятся к бактериям класса Mollicutes и являются самыми мелкими прокариотами. Они не имеют ригидной клеточной стенки, её роль выполняет трёхслойная цитоплазматическая мембрана. С отсутствием клеточной стенки связаны уникальные биологические особенности микоплазм, такие как полиморфизм, множественные способы репродукции, устойчивость к препаратам, воздействующим на клеточную стенку, и другие [2]. Человек является естественным хозяином по крайней мере 16 видов микоплазм, большинство из которых – комменсалы, но 6 видов: Mycoplasma pneumoniaе, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma spp. и Mycoplasma fermentans обладают вирулентными свойствами и достаточно часто становятся причиной развития воспалительных патологических процессов в органах мочеполовой и респираторной систем [3–6]. Микоплазмы вызывают заболевания респираторного и урогенитального трактов человека. Основным возбудителем респираторного микоплазмоза является M. pneumoniaе. Микроорганизм поражает верхние дыхательные пути с развитием фарингита, бронхита, атипичной пневмонии. M. pneumoniaе служит этиологическим фактором 10–25% острых респираторных заболеваний и 6–25% пневмоний [7, 8].
Несмотря на актуальность проблемы, в отечественной литературе мы не нашли сведений о выявлении микоплазменных инфекций после трансплантации органов.
Целью настоящей работы является выявление маркеров микоплазм у реципиентов солидных органов.
Материалы и методы
Материалом для лабораторных исследований служили образцы сыворотки крови, полученные при проведении клинико-лабораторных исследований пациентов трансплантологического профиля. Всего обследовано 99 пациентов. 1-ю группу составили 86 больных с легким течением послеоперационного периода, обследованных в различные сроки после трансплантации. Пациенты перенесли разные виды операций: ортотопическую трансплантацию сердца (ОТТС) – 44 человека, ортотопическую трансплантацию печени (ОТТП) – 9 человек, родственную трансплантацию фрагмента печени (ТФРП) – 29 человек, прочие трансплантации – 4 человека. Во 2-ю группу были включены 13 пациентов c тяжелым течением послеоперационного периода. Исследования проведены в отделении реанимации и интенсивной терапии, кардиохирургическом и абдоминально-хирургических отделениях ФГБУ «Федеральный научный центр трансплантологии и искусственных органов им. В.И. Шумакова» Минздрава России (Москва). Специфические микробиологические исследования проводили в лаборатории микоплазм и L-форм бактерий ФГБУ «Федеральный научно-исследовательский центр эпидемиологии и микробиологии им. почетного академика Н.Ф. Гамалеи» Минздрава России (Москва). Пробы сыворотки крови пациентов исследовали на наличие антигенов следующих видов микоплазм: M. pneumoniaе, M. hominis, U. spp. и антител к ним. Антигены выявляли в реакции агрегат-гемагглютинации (РАГА), антитела – в реакции пассивной гемагглютинации (РПГА). Для выявления уреаплазм использовали антисыворотку к антигенам двух видов уреаплазм. Методы постановки реакций и методы приготовления гипериммунных сывороток крови, используемых при проведении этих реакций, подробно описаны И.В. Раковской [3].
Статистическую обработку полученных результатов проводили с использованием программного пакета STATISTICA 10 («Stat Soft», США). Анализ данных осуществлялся с применением параметрического t-критерия Стьюдента. Для обозначения статистической значимости выбран уровень р < 0,05 (общепринятый для медицинских исследований).
Результаты и обсуждение
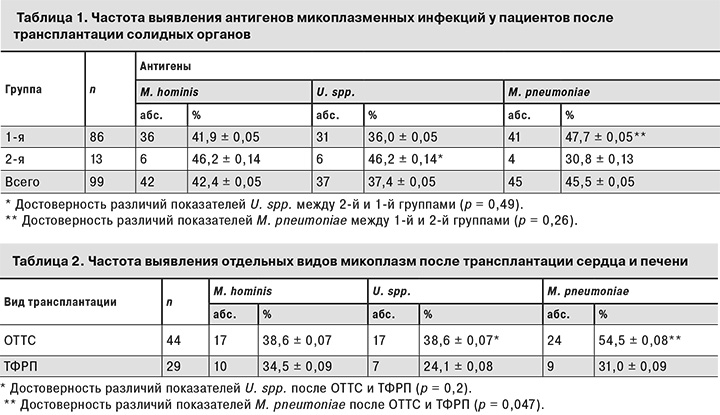
В табл. 1 представлены полученные нами данные о частоте выявления антигенов микоплазменных инфекций у пациентов после трансплантации солидных органов.
Результаты свидетельствуют о том, что U. spp. чаще обнаруживали во 2-й группе по сравнению с 1-й, а M. pneumoniae, напротив, чаще находили у пациентов 1-й группы.
Данные о частоте обнаружения микоплазм у пациентов после трансплантации сердца и фрагмента печени от родственного донора представлены в табл. 2.
Как видно из табл. 2, антигены M. pneumoniaе у пациентов после ОТТС выявляли в 1,8 раза чаще, чем после ТФРП. Уреаплазмы также преобладали у больных после ОТТС по сравнению с пациентами после ТФРП. Эти данные статистически не достоверны, хотя тенденция прослеживается.
Антитела к разным видам микоплазм без обнаружения антигена найдены у 5 взрослых больных после ОТТС. Связаны ли они с инфекцией или носительством, определить в нашем предварительном исследовании не было возможности. Таким образом, у обследованных нами 99 пациентов после трансплантации сердца, фрагмента печени, трупной печени, почек частота выявления микоплазм в зависимости от их вида составила от 37,4 до 45,5%.
Обсуждение
Выявлению микоплазменных инфекций после трансплантации органов посвящены немногочисленные работы зарубежных авторов. Согласно результатам их исследований, после трансплантации наблюдаются разнообразные по клиническим проявлениям и степени тяжести формы микоплазменной инфекции. Клиническая картина инфекции неспецифична и, как правило, не отличается от проявлений инфекций, вызванных другими микроорганизмами.
G. Lui и соавт. [9] при обследовании 279 детей и подростков на фоне атипичной пневмонии микоплазмы были обнаружены в 8% больных; при обследовании 1193 взрослых пациентов с диагнозом «внебольничная пневмония» возбудители бактериальной и вирусной этиологии выявлены у 468 (39,2%). В исследовании F. Daxbock и соавт. [10] возбудители атипичной пневмонии обнаружены в 28,6% случаев, из них микоплазмы составляли 97,8%. U. spp, M. genitalium, M. hominis вызывают воспалительные заболевания урогенитального тракта человека: уретрит, пиелонефрит, вагинит и др. [11]. Источником инфекции является больной или здоровый носитель микробов. Для микоплазменных инфекций характерна длительная персистенция возбудителя в инфицированном организме. M. hominis была выделена из мочи у 2% обследованных лиц старше 50 лет и у 6% лиц моложе 50 лет, не имевших симптомов заболевания и признаков воспаления. M. fermentans выделена из мочи у 20% здоровых студентов-медиков [12].
В настоящее время к категории риска развития микоплазменных инфекций относят реципиентов жизненно важных органов: сердца, легких, печени, почек, что является одной из проблем трансплантологии. При пересадке зараженного микоплазмами донорского органа заболевание у реципиента на фоне иммуносупрессивной терапии развивается стремительно и в большинстве случаев без своевременной этиотропной терапии заканчивается смертью пациента [13]. Микоплазмы могут вызывать абсцессы органов, медиастиниты, перикардиты, пневмонии, сепсис.
Урогенитальные микоплазмы (уреаплазмы) передаются контактно-бытовым путем. M. hominis обнаруживают во влагалище менее чем у 10% здоровых женщин, U. urealyticum – значительно чаще: по некоторым данным, у 50% здоровых женщин. Микоплазменное носительство у клинически здоровых людей представляет потенциальную опасность, так как при некоторых условиях (сопутствующие инфекции, стероидная терапия и др.) микоплазмы могут активизироваться и стать причиной септических процессов.
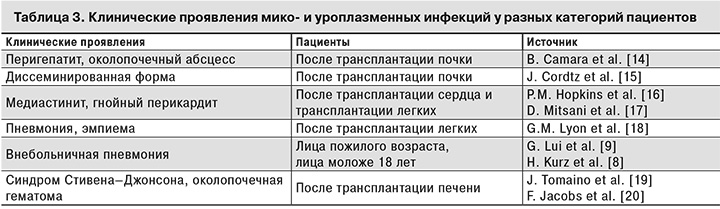
В табл. 3 представлены данные зарубежных исследователей о клинических проявлениях мико- и уреаплазменной инфекций у реципиентов органов.
Анализ полученных результатов свидетельствует о необходимости рекомендовать разработку схемы лабораторного мониторинга микоплазменной инфекции для оптимизации ее диагностики у реципиентов солидных органов. Ранняя диагностика будет способствовать своевременному назначению соответствующей антибиотикотерапии. Препаратами выбора при этитропной терапии являются тетрациклины, макролиды и фторхинолоны [19, 20]. При микоплазменной пневмонии эффективно применение макролидов и тетрациклинов. Продолжительность этиотропной терапии не зависит от выявления маркеров M. pneumoniaе, так как после проведенного лечения антигены и антитела к ним могут длительно сохраняться в организме больного. Продолжительность терапии должна определяться клиническими, а не лабораторными критериями. В этой связи интересны данные, опубликованные D. Mitsani и соавт. [17] и G.M. Lyon и соавт. [18], согласно которым реципиенты солидных органов, получавшие препараты, эффективные против урогенитальных и респираторных микоплазм (доксициклин, клиндамицин, ципрофлоксацин, азитромицин), имели минимальный риск развития микоплазменной инфекции.
Заключение
Анализ данных литературы и результаты собственных исследований свидетельствуют о важности проблемы микоплазменных инфекций для клинической трансплантологии. Не вызывает сомнения необходимость продолжения детальных клинических наблюдений, в частности, проведение обследования реципиентов и донорского материала на наличие антигенов и антител к микоплазмам перед трансплантацией и в посттрансплантационном периоде. Это важно как для профилактики и лечения острой мико- или уроплазменной инфекции в раннем госпитальном периоде, так и для предупреждения поздних осложнений. Необходимо обратить внимание на то, что микоплазмы могут способствовать непрямому повреждению тканей, вызывая усиление клеточных реакций, а также повышая чувствительность клеток к вирусам, которые интенсивно размножаются в делящихся клетках. Последнее может быть предиктором развития вирусных и бактериальных инфекций, онкологических заболеваний, дисфункии и отторжения трансплантата. Разработка алгоритма клинико-лабораторного обследования доноров и реципиентов в разные сроки после трансплантации даст возможность получить материал для формирования научно обоснованных систем лабораторного мониторинга, лекарственной профилактики и лечения пациентов трансплантологического профиля.


