На рубеже ХХ–ХХI веков в России и в ряде других стран отмечен значительный рост заболеваемости инфекциями, передаваемыми половым путем (ИППП) [1–7]. Особенно резко увеличились показатели заболеваемости сифилисом. Если до начала подъема (1988–1989 гг.) этот показатель в Российской Федерации составлял 4,3 на 100 тыс. населения, то во время пика заболеваемости (1997 г.) он увеличился более чем в 60 раз и достиг 277,3 на 100 тыс. населения. Заболеваемость гонореей в России в начале 1990-х годов возросла более чем в 2 раза: со 105 на 100 тыс. населения в 1987 г. до 232 — в 1993 г. [3, 8, 9]. В дальнейшем наблюдалось постепенное снижение заболеваемости ИППП, но по некоторым нозологическим формам, прежде всего по сифилису, показатели остаются на более высоком уровне, чем до начала эпидемического подъема [10–12].
 Периодические подъемы и спады заболеваемости ИППП считаются характерной эпидемиологической особенностью этой группы инфекций [8]. Необычно высокий подъем заболеваемости сифилисом в России связывают с социально-экономическим кризисом, по мере выхода из которого эпидемия пошла на убыль. Среди основных причинных факторов фигурируют рост безработицы, снижение жизненного уровня и миграция населения, распространение проституции и наркомании [12–15]. Очевидно, что изменение экономического базиса общества меняет поведение больших групп населения и в последующем сказывается на жизненной траектории целых поколений. Отдельные аспекты этого влияния можно проследить, анализируя динамику показателей заболеваемости ИППП. Понимание того, за счет каких социальных слоев населения формируются группы высокого риска в разные отрезки времени, имеет важное эпидемиологическое значение.
Периодические подъемы и спады заболеваемости ИППП считаются характерной эпидемиологической особенностью этой группы инфекций [8]. Необычно высокий подъем заболеваемости сифилисом в России связывают с социально-экономическим кризисом, по мере выхода из которого эпидемия пошла на убыль. Среди основных причинных факторов фигурируют рост безработицы, снижение жизненного уровня и миграция населения, распространение проституции и наркомании [12–15]. Очевидно, что изменение экономического базиса общества меняет поведение больших групп населения и в последующем сказывается на жизненной траектории целых поколений. Отдельные аспекты этого влияния можно проследить, анализируя динамику показателей заболеваемости ИППП. Понимание того, за счет каких социальных слоев населения формируются группы высокого риска в разные отрезки времени, имеет важное эпидемиологическое значение.
Известно, что в среднем сифилис и гонорея регистрируются чаще у мужчин, чем у женщин, а к наиболее уязвимой группе относятся люди в возрасте от 20 до 40 лет [8, 9]. Однако в зависимости от конкретных условий структура заболеваемости может значительно варьировать. Так, в начале текущей эпидемии ИППП в России многие исследователи отмечали увеличение доли подростков и молодежи [3, 13, 15–18]. В ряде европейских стран сифилис стали чаще регистрировать среди мужчин в результате увеличения случаев заражения при гомосексуальных контактах [5, 6].
Цель исследования – на основании статистических данных по одному из регионов России проследить, какие группы населения (по полу, возрасту, месту жительства) вносили основной вклад в заболеваемость сифилисом и гонореей на разных этапах развития эпидемии.
Материал и методы
Проведено ретроспективное описательное эпидемиологическое исследование. Использовали данные официальной регистрации впервые выявленных случаев сифилиса и гонококковой инфекции из годовых форм статистической отчетности № 2 («Сведения об инфекционных и паразитарных заболеваниях») и № 9 («Сведения о заболевании инфекциями, передаваемыми половым путем и заразными кожными болезнями») за 1988–2013 гг. Сравнивали показатели впервые выявленной заболеваемости сифилисом и гонореей, стратифицированные по полу, возрасту и месту регистрации случаев заболевания, в ходе полного эпидемического цикла. Для этого использовали среднегодовые показатели в период максимального подъема заболеваемости этими инфекциями (1993–1997 гг.) и во время снижения заболеваемости (2005–2009 гг.). За конечную точку отсчета принят 2013 г., когда заболеваемость на нисходящей части кривой многолетней динамики достигла минимальных значений за период наблюдения. Значимость различий относительных показателей между группами оценивали по 95% доверительным интервалам (95% ДИ). Для оценки связи соотношения числа зарегистрированных случаев в разных группах с фазами цикла использовали критерий χ2. В статье значения χ2 приведены при сравнении двух отрезков времени: 1993–1997 и 2005–2009 гг.
Результаты и обсуждение
В ходе текущей эпидемии ИППП Иркутская область оказалась одной из наиболее неблагополучных территорий Российской Федерации: показатели заболеваемости сифилисом и гонореей на протяжении анализируемого периода, за исключением самого начала подъема, превышали средние по стране. Заболеваемость гонореей достигла максимума в 1993 г. Пик заболеваемости сифилисом был зарегистрирован несколько позже – в 1997 г., но отличался очень высокими показателями (432,4 на 100 тыс. населения). Период подъема заболеваемости в Иркутской области привлек внимание специалистов и нашел отражение в нескольких публикациях [9, 13, 16, 17]. Экстремально высокие показатели заболеваемости регистрировались на протяжении 2–3 лет. В дальнейшем эпидемия пошла на спад, и тенденция снижения заболеваемости обеими инфекциями сохраняется до настоящего времени. В 2013 г. показатель заболеваемости впервые выявленным сифилисом снизился до 66,4 на 100 тыс. населения, что значительно выше исходного уровня. Показатель заболеваемости впервые выявленной гонореей составил 105,6 на 100 тыс. населения и уменьшился в сравнении с началом подъема. Наблюдением охвачен полный эпидемический цикл продолжительностью около 25 лет (рис. 1). Графики динамики заболеваемости сифилисом и гонореей в этот период характеризовалась значительным сходством как между собой, так и с динамикой соответствующих показателей в Российской Федерации.
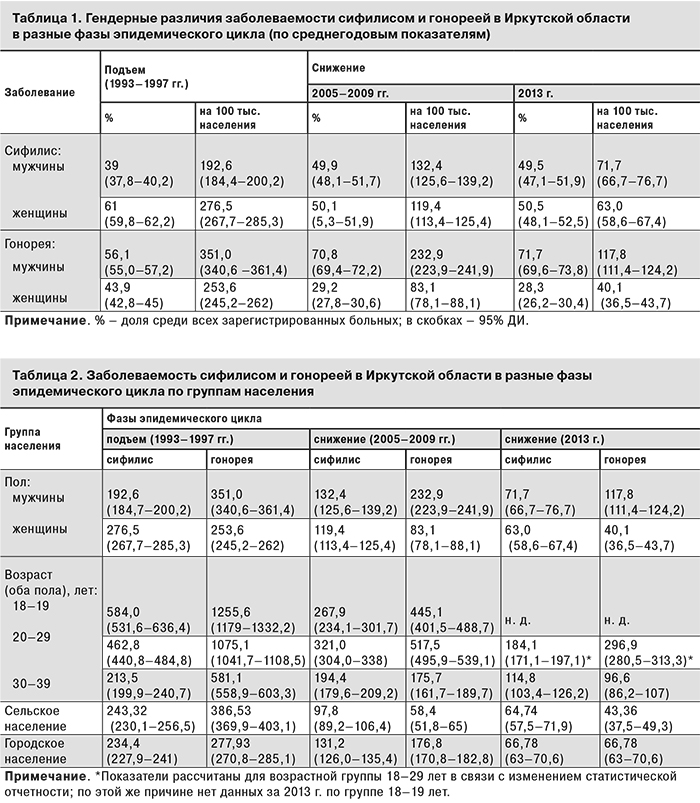
С целью сравнения групп риска для каждого из выбранных отрезков времени рассчитаны 2 показателя: доля каждой группы среди всех заболевших (в %) и частота регистрации болезни на 100 тыс. населения соответствующей категории. В качестве примера приведены результаты расчета показателей заболеваемости среди мужчин и женщин (табл. 1).
Данные о частоте регистрации (инцидентности) сведены в общую таблицу для оценки риска заболевания (табл. 2).
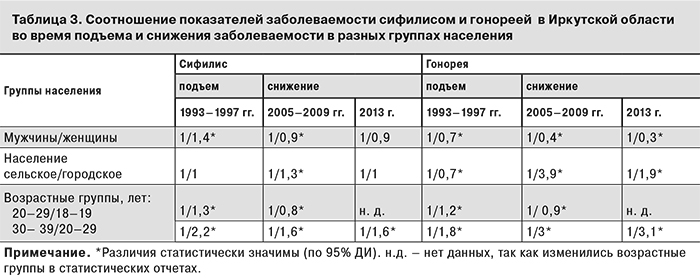
Для более наглядного представления этих данных рассчитаны показатели соотношения между группами в разные фазы цикла (табл. 3).
 Из представленных данных видно, что группы риска заболевания сифилисом и гонореей во многих случаях статистически значимо различались по полу, возрасту и месту регистрации пациентов. Но в то же время прослеживались общие тенденции по фазам эпидемического цикла.
Из представленных данных видно, что группы риска заболевания сифилисом и гонореей во многих случаях статистически значимо различались по полу, возрасту и месту регистрации пациентов. Но в то же время прослеживались общие тенденции по фазам эпидемического цикла.
Гендерные различия. Заболеваемость сифилисом среди женщин превышала заболеваемость среди мужчин в фазе подъема, но существенно не различалась в период снижения. Показатели заболеваемости гонореей у мужчин, как и ожидалось, были выше, чем у женщин на всех этапах развития эпидемии, но в фазе подъема мужчины составляли лишь немногим более половины всех зарегистрированных больных, а на нисходящей части кривой – около 70%. В то же время на их долю приходилось всего около 40% зарегистрированных случаев сифилиса в период подъема заболеваемости и около 50% – в дальнейшем. Интенсивные показатели еще более отчетливо демонстрировали гендерные различия заболеваемости в разные фазы эпидемии (см. табл. 1 и 2). Таким образом, в период подъема заболеваемости гонорея и особенно сифилис среди женщин регистрировались относительно чаще, чем во время снижения заболеваемости. На нисходящей части кривой гендерные различия заболеваемости сифилисом уменьшились, а различия заболеваемости гонореей, наоборот, возросли. Различия между фазами подъема и снижения по соотношению числа зарегистрированных случаев среди мужчин и женщин были высоко значимы для сифилиса (χ2 = 76,9; р < 0,01) и особенно – для гонореи (χ2 = 238,3; р < 0,01).
Возрастные различия. В структуре заболеваемости, независимо от фазы эпидемии, лидировала возрастная группа 20–29 лет. На ее долю приходилось 44–45% всех зарегистрированных случаев сифилиса и от 45 до 60% случаев гонореи. Однако показатель частоты заболевания в разных возрастных группах заметно менялся на разных этапах эпидемии. В период подъема наиболее высокая заболеваемость обеими инфекциями отмечена в возрастной группе 18–19 лет, а в период спада эпидемии – в группе 20–29 лет (рис. 2). Различия в соотношении числа случаев в разные фазы статистически значимы и для сифилиса (χ2 = 29,4; р <0,01), и для гонореи (χ2 = 31,5; р < 0,01). Сравнение данных 1994–1997 и 2005–2009 гг. показало, что инцидентность сифилиса статистически значимо снизилась не только в группе 18–19 лет, но и среди подростков 15–17 лет. Показатели заболеваемости сифилисом в этой возрастной группе уменьшились с 257,1 (95% ДИ 229,7–284,5) до 111,4 (95% ДИ 92,6–130,2) на 100 тыс. населения данной возрастной группы, гонореей – с 378,9 (95% ДИ 345,7–412,1) до 130,1 (95% ДИ 109,7–150,5) соответственно. Аналогичная тенденция отмечена в Российской Федерации в целом [18]. Таким образом, в фазе подъема максимальные показатели заболеваемости сифилисом и гонореей регистрировалась среди подростков и молодежи до 20 лет, через 8–10 лет после пика – среди молодых людей в возрасте 20–29 лет. К 2013 г. это соотношение существенно не изменилось.
Различия по месту регистрации заболевших. В структуре заболеваемости сифилисом и гонореей в Иркутской области в разные фазы эпидемического цикла преобладало городское население. Одна из причин – 5-кратная разница в численности городского и сельского населения. Доля горожан среди больных сифилисом составляла от 78,8% (95% ДИ 77,8– 79,8) на подъеме до 85,5% (95% ДИ 84,1–86,9) в фазе снижения, среди больных гонореей – от 91,9% (95% ДИ 91,5–92,3) до 88,4% (95% ДИ 87,0–89,8) соответственно. Однако соотношение показателей частоты заболеваемости сельского и городского населения выглядело совершенно иначе. В период подъема заболеваемость гонореей была выше среди сельского населения, а заболеваемость сифилисом среди горожан и сельских жителей статистически не различалась. В фазе снижения (через 8–10 лет после пиковых показателей) частота регистрации обеих инфекций оказалась выше среди горожан. К концу периода наблюдения (2013 г.) различия уменьшились, но гонорея среди городского населения по-прежнему регистрировалась чаще, а сифилис – практически с той же частотой, как и среди сельских жителей. Таким образом, в период максимального подъема заболеваемости обе инфекции относительно чаще регистрировались среди сельского населения, чем во время снижения заболеваемости (χ2 = 30,2; р < 0,01 и χ2 = 546,0; р < 0,01 соответственно).
Ретроспективный эпидемиологический анализ показателей заболеваемости, стратифицированных по полу, возрасту и месту регистрации заболевших, а также в зависимости от фазы эпидемии, позволяет сделать следующие предположения в отношении движущих сил значительного подъема заболеваемости сифилисом и гонореей в Иркутской области в конце ХХ века. В результате изменения социально-экономического уклада общества и глубокого экономического кризиса в первую очередь изменился образ жизни молодежи. В связи с формированием рынка сексуальных услуг наиболее уязвимой группой оказались молодые женщины. На это указывают более высокие показатели заболеваемости среди женщин и максимальные – среди подростков и молодежи в возрасте до 20 лет. В эпидемический процесс было вовлечено поколение, родившееся в конце 1970-х – первой половине 1980-х годов. Примерно через 10 лет после того, как эпидемия пошла на убыль, заболеваемость оказалась максимальной среди 20–30-летних. По-видимому, молодые люди, служившие «локомотивом» эпидемического подъема, повзрослев, перешли в следующую возрастную группу, но сохранили при этом негативные стереотипы поведения. Сходные изменения возрастной структуры заболеваемости в этот период описаны для ВИЧ-инфекции, стартовавшей в Иркутской области в 1999 г. [19]. На фоне высокой заболеваемости сифилисом и гонореей в Иркутской области реже заключались браки и регистрировались низкие показатели рождаемости [20]. Увеличение заболеваемости сифилисом и гонореей среди сельского населения в фазе подъема на первый взгляд парадоксально. По-видимому, этот феномен объясняется регистрацией случаев болезни по месту прописки. Известно, что в годы перестройки во многих регионах России усилился отток молодых людей из сельской местности, которые, не имея городской прописки, в случае заболевания регистрировались как сельские жители. Постепенный переход их в другой статус мог способствовать росту показателей заболеваемости среди городского населения в фазе снижения эпидемического процесса.
Полученные результаты позволяют наметить направления социологических исследований для количественной характеристики значимых для эпидемиологии ИППП социальных процессов. Основной вывод заключается в том, что поколение, наиболее активно участвовавшее в распространении сифилиса в начале эпидемии, продолжало вносить существенный вклад в распространение обеих инфекций в период снижения заболеваемости. Динамические изменения состава групп риска заражения ИППП следует учитывать при организации профилактических мероприятий.


